TL;DR
You will learn how to add agentic crypto payments as an automation and settlement layer, not a replacement for ACH, SWIFT, cards, or core banking. The article shows how programmable, conditional execution boosts payment intelligence, speed, and accuracy while also preserving customer experience, regulatory compliance, and current workflows.
Fintechs and financial institutions face increasing pressure to improve the speed, efficiency, and intelligence of payments. Consumers increasingly expect to receive instant payments experiences; regulators also want greater transparency and control over payments, as discussed in this guide. However, it is difficult for FIs and fintechs to completely replace existing payment systems (e.g., ACH, SWIFT, and card networks) in which these systems are embedded within FI's operational processes, regulatory requirements, and reporting obligations.
Agentic Crypto Payments provide an alternative solution that can coexist alongside legacy payment systems by providing a second layer of payment automation and settlement via blockchain and AI agents executing payments according to predetermined rules.
The purpose of this article is to describe Agentic Crypto Payments, explain why so many rail replacement projects have failed, describe how Agentic Payment Systems can be used to connect to current payment rails, demonstrate the support provided by Agentic Payment Systems to FI's compliance and reconciliation functions, and illustrate the application of Agentic Payment Systems to real-world use cases.
WHAT IS AGENTIC CRYPTO PAYMENT?
Agentic crypto payments merge blockchain settlement with AI agents. These agents can start, carry out, and reconcile payments by following set rules. Agentic systems act as an orchestration and automation layer within a financial application, as discussed in this reference.
There are no new rails when we talk about agentic crypto payments. Agentic crypto payments are not meant to replace the ACH system, SWIFT system, Card Networks or Core Banking Systems. What Agentic Crypto Payments are designed to do is provide an orchestration and automation layer at the Application Level; Payment Settlement can be done using the crypto infrastructure (for example, using a controlled blockchain environment) and remain fully compatible with all existing bank gateways and payment APIs.
Agentic Crypto Payments consist of:
A Blockchain-Based Settlement Layer
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Agents That Can Function Inside Financial Applications
The AI Agent have the ability to:
Observe certain events such as an invoice being created, an approval being granted, or an account balance being changed
Create a Payment Transaction According To Business Rules
Ask For A Cryptographic Approval Before The Payment Is Executed
Document And Reconcile All Transactions In A Standardized Auditable Format
Programmable (agentic) crypto payments include three main attributes; rule-based programmability for payment execution, a method of providing a clear and verifiable approval through cryptography, and structured payment data for easier reconciliation/reporting; while still allowing non-destructive integration into legacy payment systems. This will enable banks/institutions to "modernize" their payment processing without altering their traditional banking/financial infrastructure.
WHY REPLACING PAYMENT RAILS FAILS IN PRACTICE
Most modernization initiatives are about replacing current payment rails with new technologies. However, most of these attempts have failed or are just a small pilot.
These are some of the primary causes for that failure:
1. Deep Embeddedness in Legal & Operational Workflows
The ACH, SWIFT, and card networks all operate as part of the regulatory work flow (licensing, risk management) and operational workflow (AML/KYC, reporting etc.) and therefore changing the rail will involve many different internal departments and/or external partners.
2. High Migration Cost and Complexity
Rail replacement requires that you obtain new licenses for your vendors (and their systems), switch from one vendor to another, rewrite system code for your business, and change processes. This becomes a multi year project requiring a budget of hundreds of millions of dollars to spend, along with many delays.
3. Customer and Stakeholder Risk
Any serious disruption to payments harms customers, partners, and regulators’ trust. Institutions tend to be conservative and avoid large-scale changes that could fail in production.
4. Limited Production Impact of Pilots
Most “new rail” pilots occur in either a sandbox environment (a testing environment), or limited usage (i.e., they do not take over volume).
Industry data supports this reality:
According to an estimate made in 2023, global payment revenues were approximately $2.4 trillion in 2023. Much of these revenues go through rails which have been in existence for decades (e.g., SWIFT, card networks).
SWIFT connects over 11,000 institutions globally, with daily messaging volumes in the tens of millions.
ACH in the United States processes tens of billions of payments annually, including payroll, bill payments, and B2B transfers.
Because of this scale and integration, full replacement is not realistic for most institutions in the near term. The more practical approach is augmentation: adding intelligence on top of existing rails rather than removing them.
WHY INSTITUTIONS NEED AUGMENTATION, NOT REPLACEMENT
The financial services industry has an abundance of payment rails; however, it is lacking in terms of programmable, flexible layers atop these rails.
Financial services institutions require:
1. Automation: The ability to execute payments autonomously upon meeting specified criteria for approval, balance etc.
2. Conditioned Payments: Payments made based on specific conditions (i.e., an approval, a certain score, an event, etc.)
3. Real-time Reconciliations: The immediate verification and reconciliation of all payment related events against the financial institution's account and ledgers.
4. Clearly Stated Approvals: A clearly stated, cryptographic proof of who approved each payment and what rules were used to approve them; this is particularly important in situations where AI is used to facilitate approval.
These needs are best addressed at the application layer, not at the rail layer.
The increasing trend is for regulatory bodies to implement an "augmentation" approach, rather than a "replacement" approach when it comes to regulation and artificial intelligence (AI). The role of supervisors is to provide clarity and direction regarding the use of AI in the financial services industry, including establishing standards for governance, transparency, and accountability. The primary focus of regulatory bodies will be to establish principles that define how to maintain defined approval procedures, reliable auditing processes and significant human oversight regardless of the level of automation and/or AI usage by institutions.
Agentic crypto payments fit well into this evolving environment as they allow for controlled automation through their rule based execution, while providing strong auditability throughout all transactions. Most importantly, agentic crypto payments are built to function alongside traditional payment rails and compliance processes, allowing institutions to modernize their payment execution methodologies without having to disrupt either their regulatory alignment or their operational control.
HOW AGENTIC CRYPTO PAYMENTS INTEGRATE WITH EXISTING RAILS
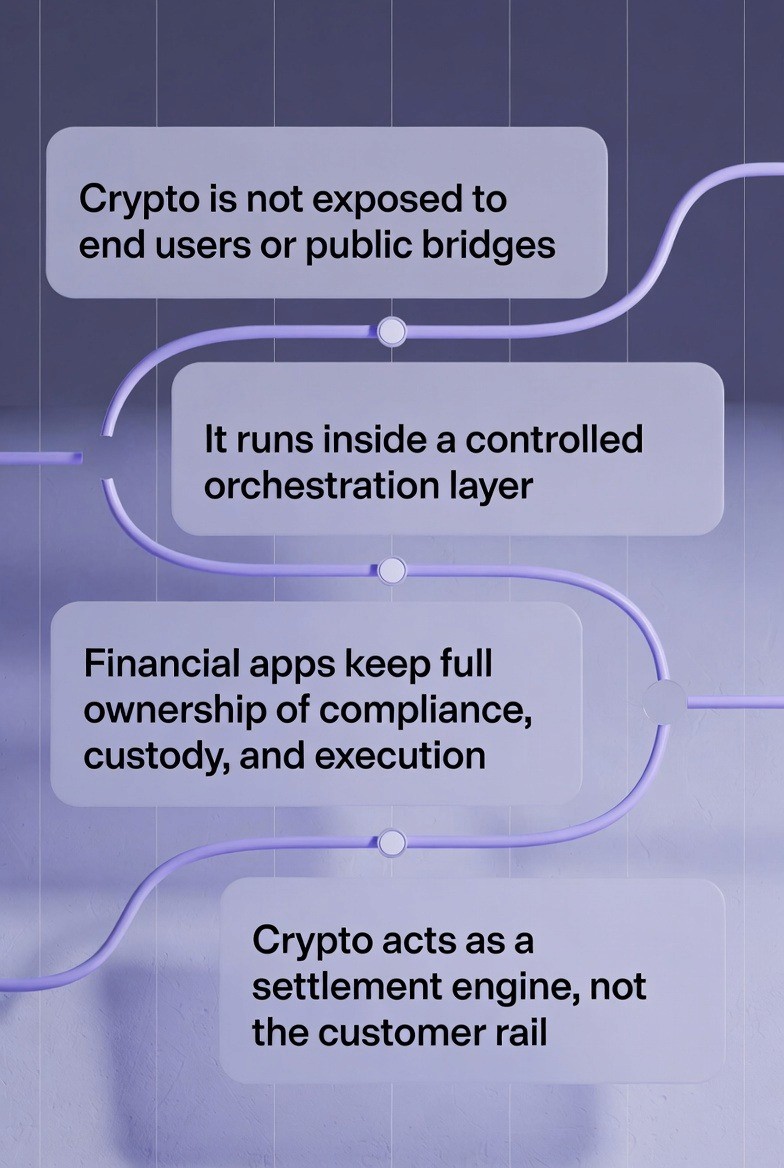
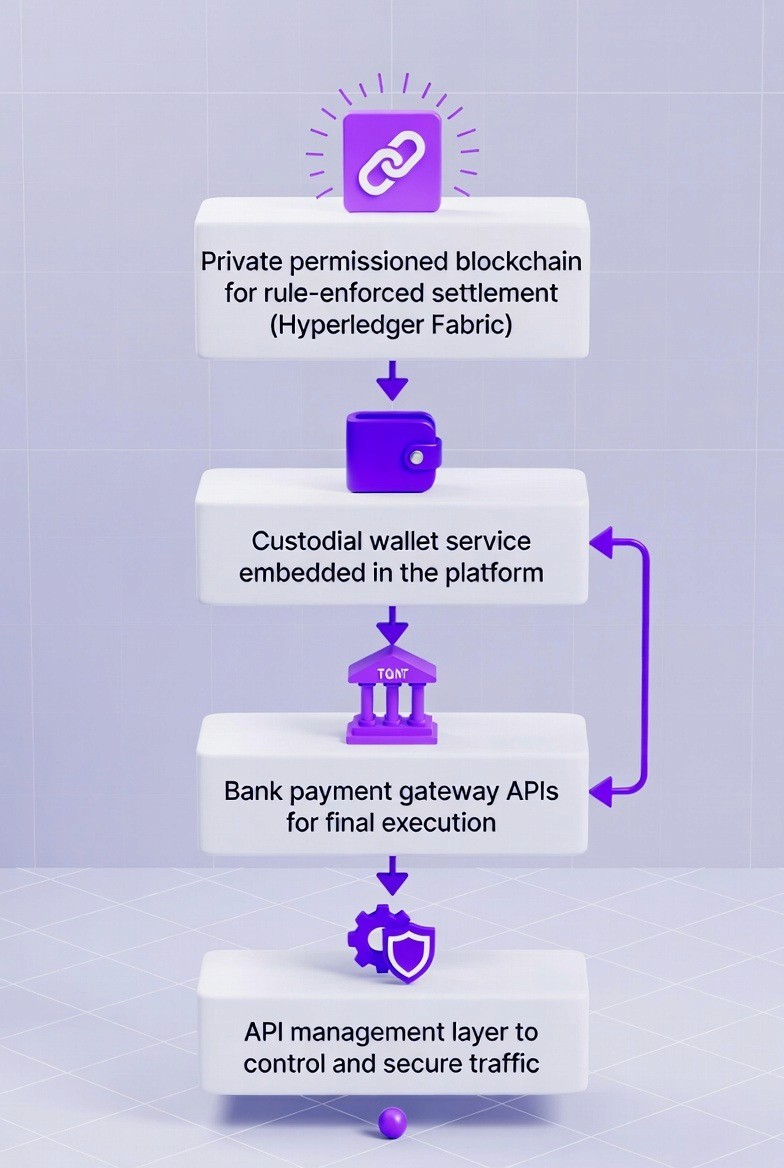
In real financial institutions deployments, crypto payments are not connected directly to consumer wallets or public bridges. They are integrated through a controlled orchestration layer that connects AI agents, private blockchain infrastructure, and bank payment gateways.
Core integration components used in production
1. A private, permissioned blockchain for enforcement of rules on settlement (Hyperledger Fabric)
The private, permissioned blockchain acts as the governed settlement layer. The smart contract (chaincode) enforces the business rules that govern how payments are made and what authorizations occur. All payments will be processed based on predetermined policies. Each approval or action taken within the system is recorded in a tamper-evident ledger to support auditing and regulatory requirements.
2. An embedded custodial wallet service within the platform
A custodial wallet service is built directly into the application and is responsible for securely managing cryptographic keys for each user and for the financial institution, as explained in this overview. This makes it easier to manage the customer's keys (thereby reducing the customer's burden) and allows for simple signing, updating balances and automatic payments in a regulated space.
3. Financial Payment Gateway APIs for Final Execution
The existing bank gateways and payment APIs are the end points for funds movement. Once a transaction has been authorized in the crypto layer, funds are settled via one of these defined channels. The use of established payment gateways, as well as APIs to effect settlements, helps ensure regulatory compliance, enables consistent and accurate financial reporting, and facilitates seamless interaction between the core system and other applications.
4. API Management Layer for Traffic Control and Security
An API management layer will connect agents, blockchain services, and banks, enforcing authentication, authorization, rate limiting, and monitoring all incoming requests to the platform. An API management layer will provide the necessary controls over the payment instruction process, ensuring that both security and compliance requirements are met at each integration point.
Crypto becomes a controlled settlement engine, while institutions retain ownership of compliance, custody, and execution.
HOW BRIDGING & CONNECTING FRAMEWORKS WORK IN PRACTICE
This is the actual connectivity stack used to integrate agentic crypto payments with financial applications infrastructure.
1) Blockchain Layer: Controlled Settlement
Hyperledger Fabric used as a private, permissioned ledger
Chaincode enforces issuance, transfer, and balance rules
Ensures transactions are confidential, deterministic, and auditable
2) Wallet & Custody Layer
Custodial wallets managed by the platform
Keys never exposed to end users or agents
Enables automatic balance and loyalty updates post-payment
3) Bank Gateway Layer
Digi-Pay wallet gateway handles bank-grade settlement
Integrated through Apigee API Gateway
Ensures crypto execution is routed through existing bank payment rails
4) API & Middleware Layer
Apigee for API management, throttling, and security
MCP services (Java) handle:
Product data
Balance updates
Loyalty state
PostgreSQL + Redis for transactional state and session control
Result:
No public bridges. No rail replacement.
Only controlled API connectivity between bank systems and crypto execution.
HOW AGENTIC ORCHESTRATION TIES EVERYTHING TOGETHER

The real innovation is not the blockchain; it is the agentic orchestration layer that connects systems safely.
Execution pattern used in production
Front-man agent guides the user journey (checkout, request, trigger)
Bank-man agent prepares the transaction on the private ledger
User provides cryptographic approval inside the flow
Transaction executes on Hyperledger Fabric
Settlement is routed through Digi-Pay via Apigee
Balances and loyalty points update automatically
What this achieves
Approval is explicit and cryptographic
Settlement is bank-grade and auditable
Post-payment state is synchronized automatically
No dependence on public chains or consumer bridges
This is how crypto payments integrate without replacing SWIFT, gateways, or core banking — by adding an agentic + private-ledger + API orchestration layer on top.
HOW SETTLEMENT AND RECONCILIATION WORK TOGETHER

Agentic payment systems treat blockchain and crypto settlement as a complementary execution layer rather than a replacement for existing infrastructure. A private or permissioned ledger can be used to run programmable payment logic, capture rich transaction metadata, and maintain verifiable records of approvals and actions.
Once execution is completed on the crypto layer, final settlement can still flow through existing bank gateways, established payment APIs, or—where appropriate; tokenized and stablecoin-based rails, allowing institutions to gain the benefits of automation and auditability without disrupting their current payment operations.
The reconciliation flow typically looks like this:
Agent Executes Payment Logic Using Crypto Settlement
The agent triggers a smart contract or ledger operation that follows the institution’s rules.Transaction Data Is Recorded and Verified
The system stores:Timestamp
Parties involved
Amount
Approval references
Rule identifier or workflow ID
Results Are Reconciled into Existing Ledgers and Reports
The system pushes normalized transaction records into:Core banking ledgers
General ledger and accounting systems
Reporting tools for finance and compliance
This process lowers manual reconciliation workload and keeps data consistent across systems.
TABLE: TYPICAL SETTLEMENT SPEED AND COST BY METHOD
Below is a simple comparison of common settlement methods and a controlled blockchain-based stablecoin settlement. Values are indicative ranges, not precise quotes.
Payment Method | Typical Settlement Time | Approximate Cost per Transaction | Availability | Typical Use Case |
Traditional SWIFT (cross-border) | 3–5 business days | USD 20–50 | Business days, cut-off times | Large cross-border bank transfers |
ACH (domestic) | 1–3 business days | USD 0–10 | Business days, batch windows | Payroll, bills, domestic B2B |
Card Networks | Same day to 2 days (merchant settlement) | 1–3% of transaction value | 24/7 authorization, settlement in batches | Retail, e-commerce |
FedNow or similar instant payment rail | Seconds to minutes | USD 0.10–0.50 | 24/7/365 | Domestic instant payments |
Blockchain Stablecoin (controlled environment) | Under 3 minutes (often seconds) | USD 0.10–1.00 | 24/7/365 | Cross-border B2B, treasury, automated flows |
This table shows why institutions are interested in combining existing rails with a programmable settlement layer. A controlled stablecoin or tokenized settlement environment can reduce settlement time from days to minutes while keeping compatibility with current systems and regulatory controls.
HOW THE CONTROL MODEL WORKS
Agentic crypto payments are designed to respect and strengthen compliance, not weaken it. The control model is based on clear boundaries and verifiable records.
Key elements of the control model include:
Pre-Approved Execution Rules
The institution defines allowed actions for each agent:Payment types (e.g., supplier payouts, refunds, internal transfers)
Approved counterparties or counterparty categories
Allowed currencies or token types
Spending and Frequency Limits
Limits are set by:Amount per transaction
Total volume per day, week, or month
Number of transactions per period
Explicit Cryptographic Approvals
Every executed payment includes:Clear identification of the approver
A cryptographic signature or equivalent proof
A binding link between the approval and the executed transaction
Full Execution Logs and Audit Trails
Each step in the payment lifecycle (preparation, approval, execution, reconciliation) is logged.
Institutions can then:
Review any transaction end-to-end
Prove that AI agents operated within allowed ranges
Show regulators how controls are implemented
Industry surveys indicate that a high percentage of financial institutions plan to deploy smart contracts and programmable logic for approvals, especially in large-value and cross-border flows. The banking sector already represents a significant share of smart contract use in regulated environments.
STACKS: PRIVATE BLOCKCHAIN (HYPERLEDGER FABRIC) FOR CONTROLLED SETTLEMENT
Hyperledger Fabric enables crypto payments to run in a permissioned, auditable, and deterministic environment. This removes the operational and regulatory risks associated with public-chain execution while preserving programmability.
For financial institutions, this creates a controlled crypto settlement zone that fits existing compliance models.
Key features:
Permissioned access and identity control
Deterministic execution and finality
Confidential transaction data
Audit-ready ledger records
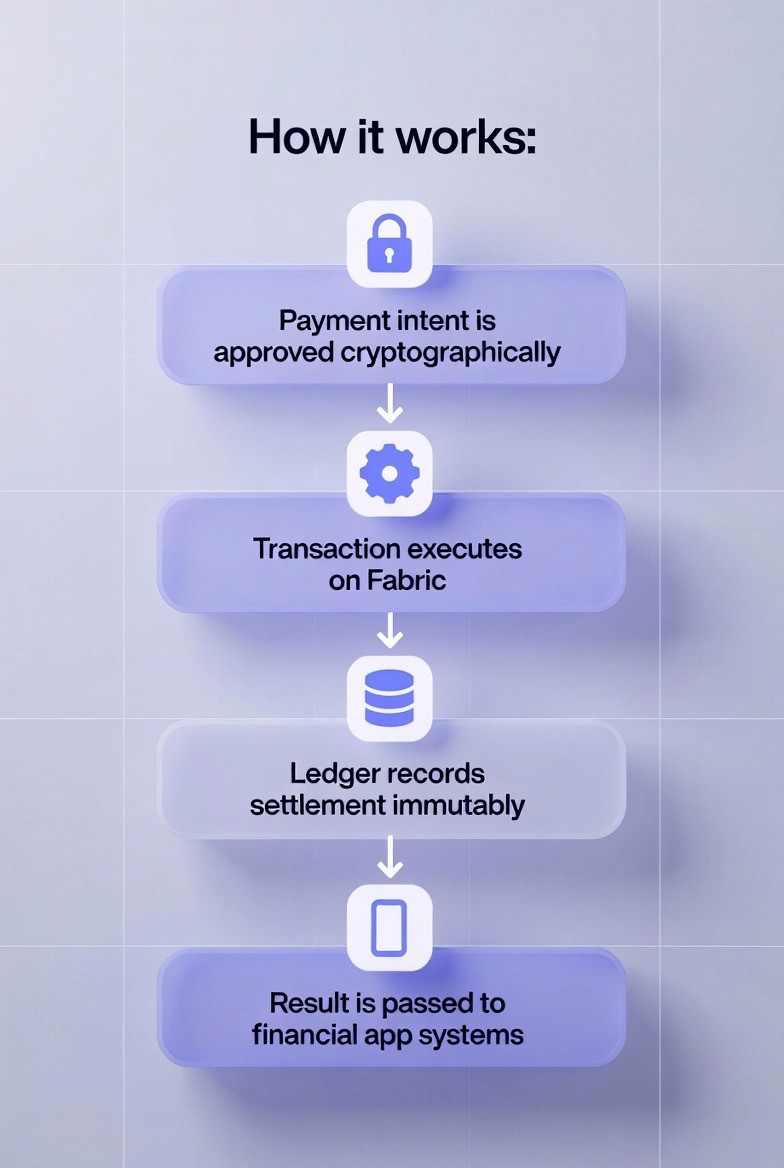
How it works:
Payment intent is approved cryptographically
Transaction executes on Fabric
Ledger records settlement immutably
Result is passed to bank systems
STACKS: CUSTODIAL WALLETS FOR SAFE KEY MANAGEMENT
Custodial wallets ensure that private keys remain under institutional control, not with AI agents or end users. This is critical for preventing unauthorized execution in agentic payment systems. It aligns crypto operations with existing custody and risk management standards.
Key features:
Centralized key custody
Role-based access control
Multi-signature support
Hardware security module (HSM) compatibility
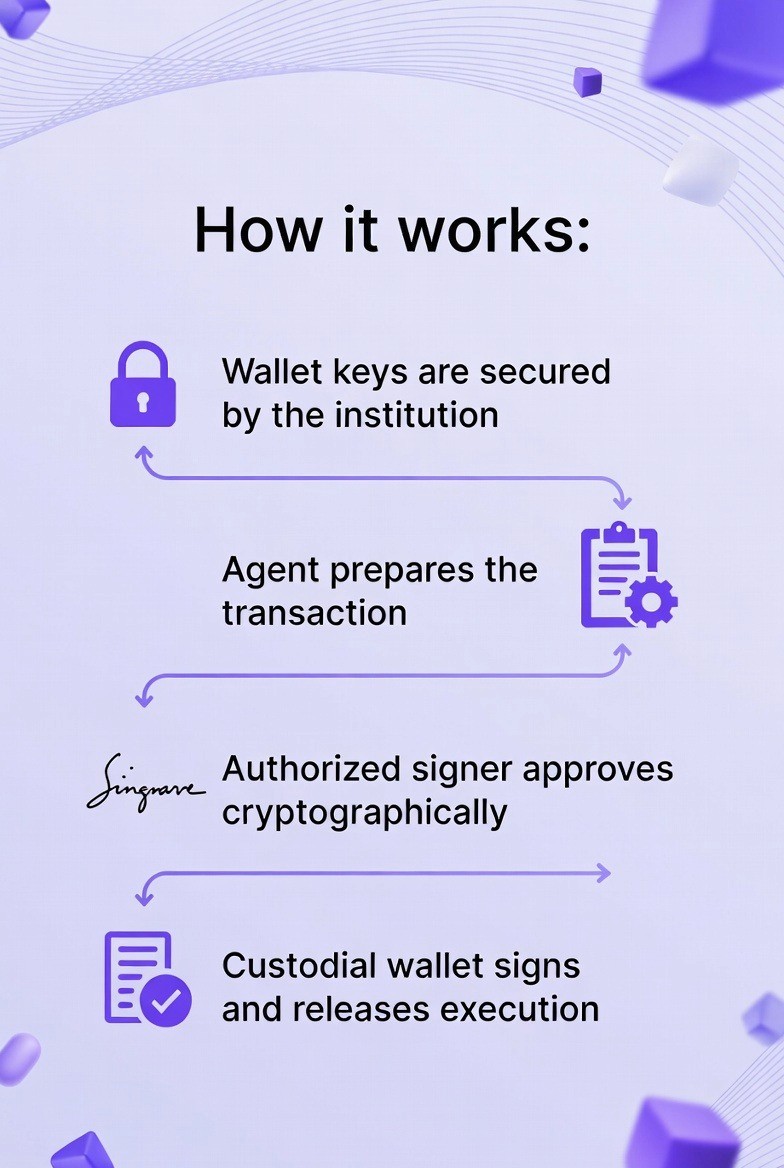
How it works:
Wallet keys are secured by the institution
Agent prepares the transaction
Authorized signer approves cryptographically
Custodial wallet signs and releases execution
STACKS: BANK GATEWAYS (DIGI-PAY) FOR EXECUTION
Bank gateways ensure that crypto payments flow through existing regulated payment infrastructure. They prevent crypto from becoming a parallel, uncontrolled settlement path. Instead, they make crypto an execution engine that feeds into bank rails.
Key features:
Integration with core banking and wallets
Compliance and transaction screening
Bank-grade reliability and uptime
Settlement through regulated channels
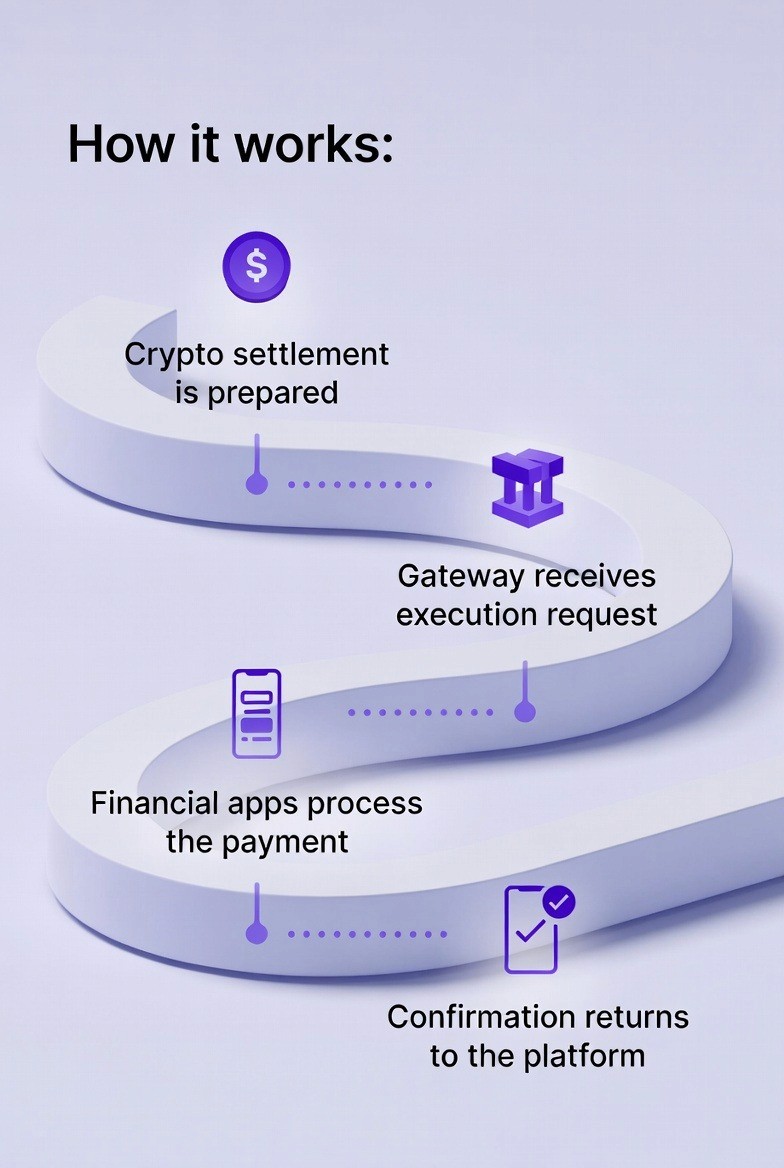
How it works:
Crypto settlement is prepared
Gateway receives execution request
Bank systems process the payment
Confirmation returns to the platform
STACKS: API MANAGEMENT (APIGEE) FOR SECURE CONNECTIVITY
API management platforms such as Apigee provide the control plane for system-to-system integration. They ensure that agentic payments do not create unmanaged connectivity between banks and crypto systems. This is where security, throttling, and governance are enforced.
Key features:
Authentication and authorization
Rate limiting and throttling
Traffic monitoring and logging
Policy enforcement at the API layer
How it works:
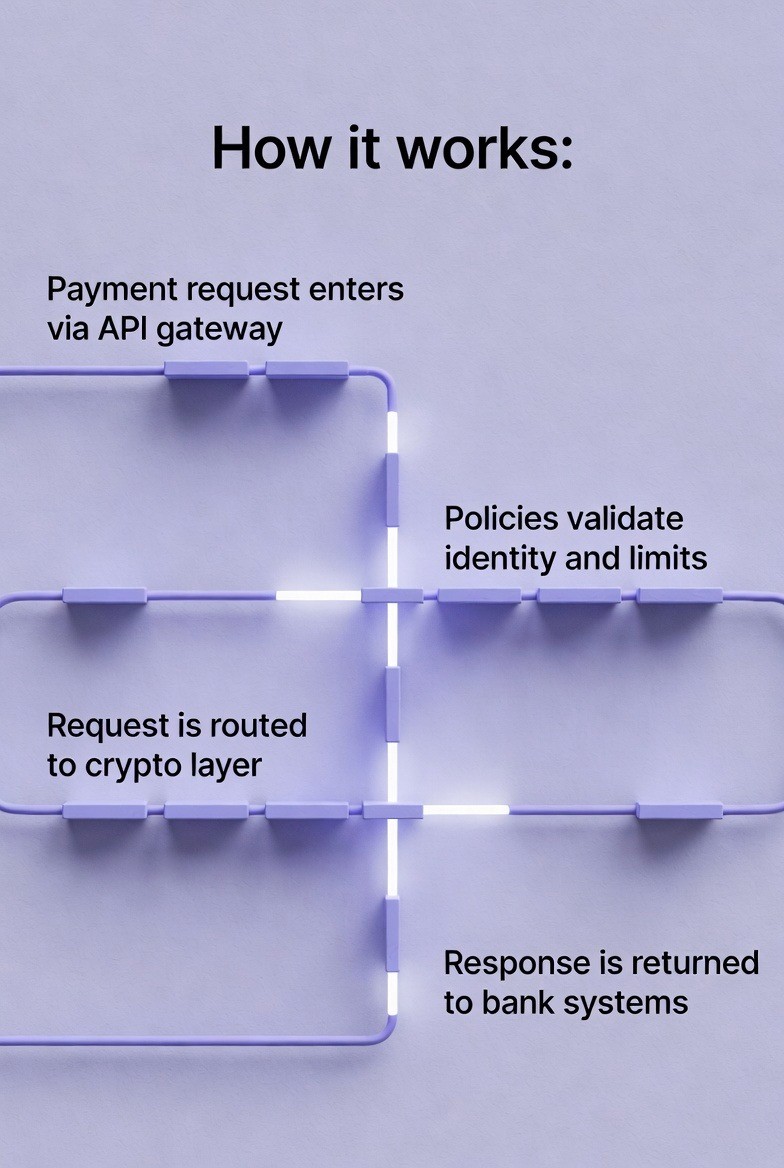
Payment request enters via API gateway
Policies validate identity and limits
Request is routed to crypto layer
Response is returned to bank systems
HOW TO INTEGRATE AGENTIC CRYPTO PAYMENTS WITH FINANCIAL APPS SYSTEMS

Crypto payments are integrated into financial applications through orchestration, not replacement. Below is the actual delivery pattern used in production environments.
STEP-BY-STEP IMPLEMENTATION
1. Anchor in the Existing Payment Flow
Start inside what already works.
Integrate at the application and gateway layer, not the rail layer.
Keep SWIFT / Digi-Pay / card / core banking untouched
Identify where payment instructions are created
Insert the agentic orchestration layer at this point
2. Deploy a Controlled Crypto Execution Environment
Never connect agents directly to public rails.
Use a private or permissioned blockchain
Enforce rules with network-level logic (or controlled smart contracts)
Enable custodial wallets for institutional key control
This becomes the crypto execution zone, not the system of record.
3. Connect Crypto to the Bank Gateway via APIs
Crypto never bypasses the bank.
Expose settlement endpoints through
API Gateway (e.g., Apigee)
Internal payment services
Route every executed crypto payment through:
existing bank wallet
or payment gateway
This ensures bank-grade settlement and compliance.
4. Insert the Agentic Orchestration Layer
Agents do not execute payments; they prepare the path.
Agent reads triggers from:
checkout
treasury system
ERP
Agent drafts the transaction on the crypto layer
Agent requests cryptographic approval
5. Enforce Explicit Cryptographic Approval
This is the control point.
User or institution signs:
transaction intent
Signature is stored as:
on-chain record
or signed message
No approval = no execution
This creates audit-grade authorization.
6. Execute Settlement Through the Bank Path
After approval:
Transaction commits on the controlled crypto ledger
Settlement is routed via:
bank gateway API
SWIFT / internal rails
Confirmation flows back to:
core banking
treasury systems
Crypto acts as execution logic, not the rail.
7. Synchronize Post-Payment State
Automation completes the loop.
Balances updated
Loyalty / rewards updated
Receipts generated
Reconciliation entries posted
All automatically; no back-office bottlenecks.
ARCHITECTURE: LAYERED MODEL FOR AGENTIC CRYPTO PAYMENTS
A practical architecture for agentic crypto payments is usually layered.
Layer 1: Existing Payment Rails
ACH
SWIFT
Card networks
Domestic instant payment systems (e.g., FedNow or equivalents)
This layer continues to function as the primary payment infrastructure.
Layer 2: Application-Level Agentic Orchestration
AI agents that monitor events and apply rules
Policy engines that hold business logic and compliance rules
Approval workflows that integrate with users and internal staff
Connectors to KYC/AML, fraud detection, and risk scoring systems
This is where agentic crypto payments “live” from a logic perspective.
Layer 3: Blockchain or Tokenized Settlement Layer
Private or permissioned blockchain environments
Stablecoin or tokenized cash instruments
Smart contracts for programmable settlement
Cryptographic signing and audit mechanisms
This layer is used for execution, verification, and data integrity.
The three layers work together:
Layer 2 decides what to do and when, following institution-defined rules.
Layer 3 executes the logic and records it in a verifiable way.
Layer 1 moves the money through channels already accepted by regulators and partners, when needed.
TABLE: STEP-BY-STEP PHASED ROLLOUT APPROACH
Phase | Scope | Typical Actions | Risk Level |
Phase 1: Design & Sandbox | No production volume | Define rules, build prototypes, test with sample data | Low |
Phase 2: Limited Pilot | Low-value, limited set of use cases and users | Run supervised pilot in production, with close monitoring | Low–Medium |
Phase 3: Controlled Expansion | More use cases, moderate values | Expand to additional segments, adjust limits and rules | Medium |
Phase 4: Scale-Up | Broader coverage, higher values | Integrate with enterprise-wide processes and multiple rails | Medium–High (managed by controls) |
This phased strategy supports risk management and aligns with regulators’ expectations for careful adoption of AI and blockchain in core processes.
REAL USE CASES AND INDUSTRY MOMENTUM

Agentic crypto payments have moved beyond experimentation and are now being implemented in real-world financial systems with production-grade controls and governance..
TokenMinds Implementation
A regulated client worked with TokenMinds to deploy a live agentic crypto payment solution:
AI agents assist shoppers inside a financial or commerce application.
When a shopper is ready to pay, the agent drafts a transaction on a private ledger.
The system then requests a simple cryptographic approval within the interface.
After approval, settlement occurs through the bank’s existing payment gateway.
Loyalty and balance updates are performed immediately.
This implementation reduced the number of steps in the checkout flow and made balances and loyalty rewards update in near real time, without changing the underlying bank rails.
Industry Pilots by Visa
Major payment networks are now validating agentic payments through real pilots, with Visa leading efforts to support agent-driven transactions using tokenized rails and stablecoin settlement. Alongside this, technology providers are introducing agent payment frameworks, and banks and fintechs are rolling out APIs for programmable payment execution—signaling that agentic crypto payments are rapidly moving from experimentation to mainstream adoption.
TABLE: SELECTED TRENDS IN BLOCKCHAIN AND CRYPTO PAYMENT ADOPTION
Indicator | 2024–2025 Trend | Relevance to Agentic Crypto Payments |
On-chain stablecoin transfer volume | Exceeded tens of trillions of USD equivalent in 2024 | Demonstrates scalability of blockchain settlement for high volumes |
Merchant crypto acceptance | Around 40–50% of surveyed merchants report using or piloting crypto payments in some markets | Shows demand for alternative rails and tokenized payments |
Share of institutions exploring smart contracts | Majority of large financial institutions report pilots or research | Provides foundation for programmable, rule-based payments |
RegTech market growth | Projected to surpass USD 20 billion mid-2020s | Indicates strong focus on technology-enabled compliance, which agentic payments can support |
These trends support the case that combining AI agents with blockchain settlement is aligned with broader industry movement, especially in large institutions and merchants.
FAQ
1. Why is replacing existing payment rails not realistic for most institutions?
ACH, SWIFT, and card networks are deeply embedded in regulations and operations. Replacing them needs multi-year programs that cost a lot, carry regulatory risk, and often have little real-world effect. Most “new rail” projects never get past the pilot stage.
2. What makes agentic crypto payments different from traditional crypto payments?
Agentic crypto payments don’t create a new rail; they add an automation and orchestration layer on existing rails. AI agents prepare, validate, and reconcile payments, using blockchain for controlled execution. Final settlements still go through bank gateways and regulated infrastructure.
3. How do agentic systems improve compliance rather than weaken it?
They provide explicit cryptographic approval, rule-based execution, and full audit trails at the application layer. Each payment links to a defined policy and a verified approver, creating a clear, tamper-evident record—more so than in manual or semi-automated workflows.
4. Why is a private or permissioned blockchain critical in this model?
Institutions need programmability without the risks of public chains. Using platforms like Hyperledger Fabric allows for predictable execution, confidential data handling, and audit-grade records—while avoiding public bridge exposure, volatile fees, and uncontrolled settlement paths.
5. What is the real architectural shift enabled by agentic crypto payments?
The shift moves from rail-centric modernization to application-centric automation. Instead of changing how money moves, institutions change decision-making—using agents, APIs, and controlled crypto execution to automate approvals, reconciliation, and reporting on trusted rails.
HOW TOKENMINDS SUPPORTS AGENTIC CRYPTO PAYMENT INTEGRATION
TokenMinds works with financial institutions and fintech companies to design and implement agentic crypto payment architectures that operate alongside existing rails. The focus is on practical, compliant, and safe deployment rather than experimentation without structure.
Core areas of support include:
Application-Layer Design
Defining how agents interact with users, internal teams, and systems.Approval and Control Models
Designing rule sets, limits, approval flows, and cryptographic authorization mechanisms.Compliance Alignment
Ensuring the architecture fits regulatory expectations and supports audit and reporting requirements.Operational Safety and Monitoring
Building dashboards, alerting systems, and incident-handling procedures.
A typical engagement follows four steps:
Assessment
Map current payment flows, systems, and constraints. Identify where agentic automation can create value without adding unacceptable risk.Design
Create architecture and rule frameworks that integrate agents, crypto settlement, and existing rails.Implementation
Build, test, and deploy the solution, starting with pilots and controlled use cases.Optimization
Collect data, refine rules, expand coverage, and improve performance and user experience.
CONCLUSION
Agentic crypto payments bring smart automation to the application layer. They keep existing systems intact while allowing for programmable execution, cryptographic approvals, and easy-to-audit data. This helps institutions modernize safely, lower operational friction, and boost compliance without disrupting trusted financial networks.
If your organization is looking to implement agentic crypto payments without changing your current setup, schedule a free consultation with TokenMinds. Our team will evaluate your payment system, pinpoint impactful use cases, and craft a secure, compliant integration strategy just for you. This way, you can confidently advance toward automated financial operations.








