TL;DV: zkSync Elastic Network is a scalable blockchain settlement technology design for banks, regulated enterprises and financials to utilize their own elastic chains as public, permissioned, or hybrids with all activity settled via Ethereum utilizing zero knowledge proof for compliance, efficiency and security.
ABOUT ELASTIC NETWORK
zkSync Elastic Network is a completely new paradigm for handling money and financial transactions. Prior to 2024, zkSync was essentially a quicker version of the Ethereum blockchain. Now, it is an entirely new system of interconnected blockchain networks working together. The interconnected blockchain network is supported by zero-knowledge technology, as outlined here, enabling secure verification while preserving confidentiality.
At its core, the Elastic Network concept is straightforward: rather than forcing all banks, companies and organizations to share the same blockchain (and thus creating potential issues), the Elastic Network enables organizations to establish their own private blockchain. Organizations can tailor their blockchain to meet their unique requirements, including rules for confidentiality, fees and who may participate on the blockchain.
Network of Customized Financial Settlement Chains
Here is the key distinction: today, large banks and institutions wanting to utilize blockchain technology have to follow the same rules as all other users of blockchain technology. This general approach is often outlined in basic development references. However, there are significant differences between the needs of large banks and those of cryptocurrency exchanges. Banks and institutions are concerned with confidentiality and compliance with regulatory requirements. Cryptocurrency exchanges are primarily interested in being fast and publicly transparent.
By enabling each organization to create a blockchain tailored to their specific requirements, the Elastic Network addresses these distinctions. The features of a blockchain that organizations may modify include:
Elastic Feature | What Organizations Can Choose |
Who Can Use It | Everyone can see and use it, or only certain people can, or a mix of both |
Privacy | Keep everything secret or make everything visible to everyone |
Who's in Charge | One company runs it, or multiple companies vote on decisions |
What Can Be Traded | Money, stocks, bonds, or any kind of digital asset |
Rules for Transfers | Create special rules about who can buy and sell what |
Ethereum As The Settling Ledger (Anchor)
What’s interesting here is that, although each organization is running on their own blockchain, ultimately, they’re all going to send proof of transactions back to Ethereum. Ethereum is the ultimate, extremely secure ledger where each and every transaction gets recorded as having occurred.
Elastic Network is working similarly. Each organization is operating its blockchain independently; however, they each send a record of the blockchain to Ethereum. Ethereum is the final authority that confirms “yes, that did happen” and no one can alter those records.
Settlement is very important in the world of finance; settlement is when a party confirms that a transaction has been completed and that the funds have changed hands. Once a transaction is settled, there is no turning back.
Each Organization Can Configure Their Blockchain
One reason why many financial institutions have avoided using blockchain technology is that regulatory bodies need to be assured that whatever actions take place on a blockchain are compliant with regulations.
Banks have thousands of laws governing the actions they may take with money, and therefore, each organization must be able to configure their blockchain in a way that complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
In the case of the Elastic Network, each organization will be able to determine who has permission to access their blockchain and who does not. Organizations can also define the rules by which the blockchain operates, i.e., “we don’t allow this type of transaction.” When the blockchain determines that an action violates its defined rules, the blockchain will prevent that transaction from being processed. These rule-based controls can also be extended across connected networks through verification mechanisms explained here.
Therefore, each organization will be able to operate their blockchain within the confines of their respective laws and regulations.
HOW ELASTIC NETWORK SUPPORTS COMPLIANT ASSET TOKENIZATION

"Tokenization" is a fancy word that means turning real-world things into digital tokens. For example, a company could tokenize a building (turn the building into a digital token worth $10 million), or create digital tokens of stocks, bonds, or gold.
The problem is that doing this with regular blockchain technology has been hard because of privacy and rules. The Elastic Network fixes this with four main features:
1. Private & Permissioned Issuance
When a bank wants to issue digital tokens of corporate bonds, they can't just put it on a public blockchain where everyone in the world can see it and try to buy it. They need to control exactly who can participate.
The Elastic Network lets banks create a blockchain where they control who gets in. The bank can say: "Only people who are wealthy enough to invest in bonds can see these bonds. Only approved dealers can buy and sell them."
This is like having a private store instead of a public store. A regular store lets anyone walk in and buy anything. A private club has a membership list and doors with guards. The Elastic Network gives banks and institutions that private club option.
2. Proof-Based Settlement
Here's something really cool: every time someone transfers a tokenized asset, the blockchain creates a mathematical proof that the transaction actually happened and followed all the rules.
In regular banking, when you transfer money, you trust your bank to record it correctly. But what if the bank makes a mistake? The only way to prove it is to have documents and paperwork from the bank.
With the Elastic Network, there's no paperwork. There's mathematical proof. This proof is something that cannot be faked or changed.
This matters for government regulators. When a bank regulator audits a bank, they don't need to ask the bank for paperwork. The bank just shows the mathematical proof, and the regulator can check it themselves.
3. Configurable Compliance Logic
Banks and financial institutions have to follow tons of rules about who can own what. Here are some examples:
Only verified people can invest in some types of bonds
You can't send money to certain countries (these countries are called "sanctioned")
No single person can own more than 25% of a company
Some assets have to wait a certain number of days before they're officially owned
Right now, banks and institutions have to make people follow these rules by reminding them, training them, and hoping they don't break the rules. But what if the rules were built into the blockchain itself?
The Elastic Network does exactly this. You can program the blockchain so that it's literally impossible to break the rules. You can't send money to a sanctioned country because the blockchain won't allow it. You can't own more than 25% of a company because the blockchain automatically stops you.
4. Privacy-Preserving Transparency
This is the coolest part, and it sounds like magic but it's just math. Here's the problem: regulations like GDPR (the European privacy law) say that companies have to protect people's private information. So a bank can't tell the government "John Smith sent $1 million to Sarah Johnson."
But the government also needs to make sure the bank isn't helping criminals. So the government needs to know that someone transferred $1 million, just not who the people were.
The Elastic Network solves this with zero-knowledge proofs. The bank can prove: "Yes, someone transferred $1 million, and the person sending it had enough money, and both people are verified customers, and no laws were broken." The bank can prove all of this without ever saying who the people are.
WHAT IS ZERO KNOWLEDGE PROOF

This is the technology that makes the Elastic Network possible, so it's important to understand it.
A zero-knowledge proof is a way to prove something is true without showing the actual information. That sounds impossible, but it's real math.
Key Features of Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
Prove Without Revealing: You can prove something is true without showing what it is. A bank can prove that a customer has $1 million in their account without revealing who the customer is or even how much money they have.
Trust without Intermediaries: Instead of trusting a bank to tell the truth, you trust the ledger. Math never lies. Math doesn't depend on money or politics—it just is what it is. This is way safer than any other options.
Independent Verification: Anyone can check the ledger themselves. A government regulator doesn't need special access to bank computers. They can just check the ledger like anyone else. This makes it harder for banks or enterprises to hide things.
Perfect for Regulated Finance: Banks and institutions need two things that seem impossible together: keeping client information secret AND proving to regulators that they're following the rules. Zero-knowledge proofs do both at the same time.
THE PROBLEM IN WEB3 FINANCE

Right now, the financial system has some really big problems. Web3 (which means using blockchain and crypto) could solve many of these problems, but it has its own problems too.
1. Fragmented Ledgers
When you send money from a U.S. bank to a European bank, the money doesn't just go directly. It goes through 5 or 6 different banks and payment systems. Each one keeps its own records. If there's a mistake, it takes forever to figure out what happened. Sometimes disputes take three weeks to resolve.
2. High Settlement Costs
Ethereum and most blockchains charge high fees. During busy times, a single transaction can cost $50 to $200 in fees. Old payment systems are cheaper but super slow (they take 3 or more business days).
3. Privacy Constraints: Banks can't put their business on public blockchains because everyone can see everything. A bank moving $100 million can't announce that to the whole world. Governments buying or selling currency can't let everyone see what they're doing.
Here's how these problems hurt different organizations:
Problem | Affected Parties | Example |
Fragmented systems | Banks, businesses | Takes 3-5 days to transfer money between banks |
High costs | Everyone | Pay $50-200 just to move money once |
Privacy issues | Governments, banks | Can't use public blockchains for sensitive money |
Regulatory issues | Banks, regulated companies | Hard to prove to auditors that rules were followed |
WHAT ENTERPRISES ACTUALLY NEED
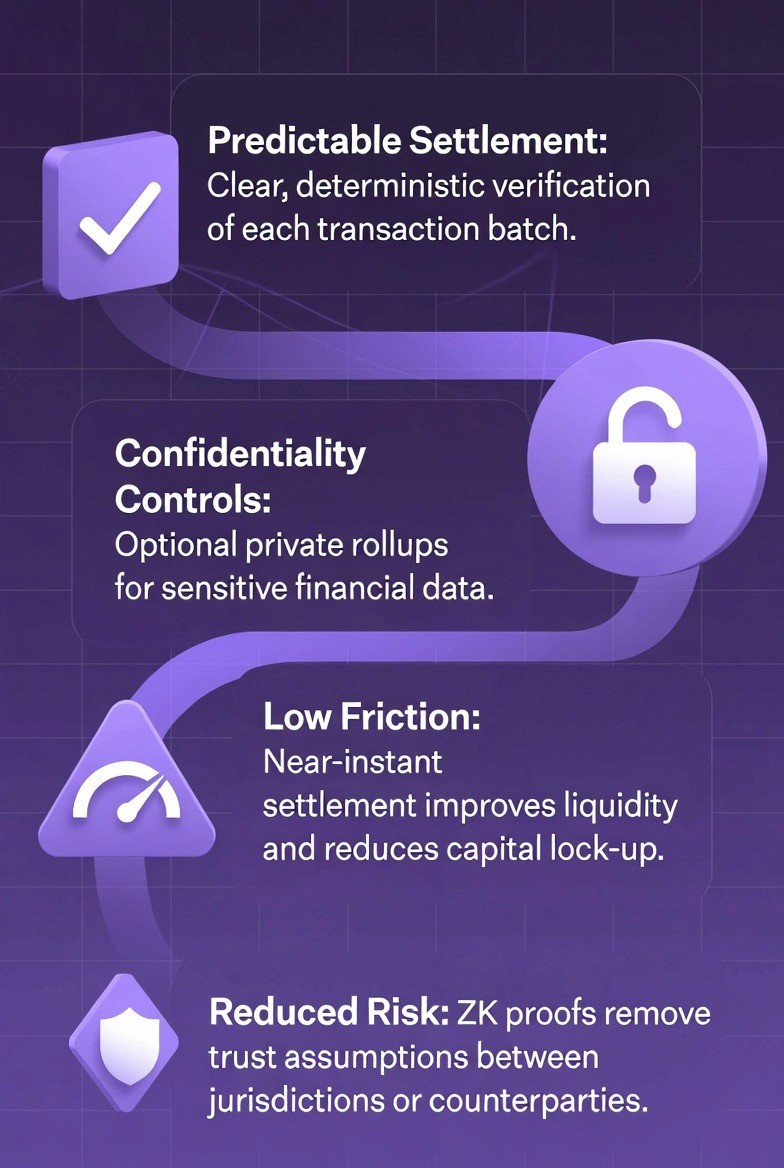
Large institutions that process large amounts of money have unique requirements. For this reason, the Elastic Network was developed to satisfy the needs of these institutions:
Settlement Predictability
Organizations need certainty as to when a transfer of funds has been completed and accepted by the intended recipient so that no additional reversal can occur. At present, uncertainty exists as to whether an individual transaction has actually concluded.
Privacy Controls
Central Banks and Investment Companies require all financial information related to their transactions to remain completely private. In other words, they cannot allow others to view what is being done with their money.
Reducing Friction
The term "friction" in finance refers to the time required for completion of a transaction, as well as the cost associated therewith. Organizations wish to conduct transfers of funds without delay and wish to know if those funds have arrived at the destination, instantaneously. Presently, many organizations hold excess funds in reserve accounts in anticipation of such delays. This reserve requirement would be greatly reduced under instant settlement.
Risk Reduction
Organizations rely on trust that their counterparties will not take advantage of them by disappearing with the organization's funds; that the system itself will not malfunction and/or lose access to data; and that their data will not be stolen. However, zero-knowledge proofs eliminate these reliance requirements by providing mathematical proof that everything has been completed correctly.
For this reason, the Elastic Network satisfies each of the needs listed above, which is why large financial institutions are interested in the Elastic Network.
HOW ELASTIC NETWORK WORKS
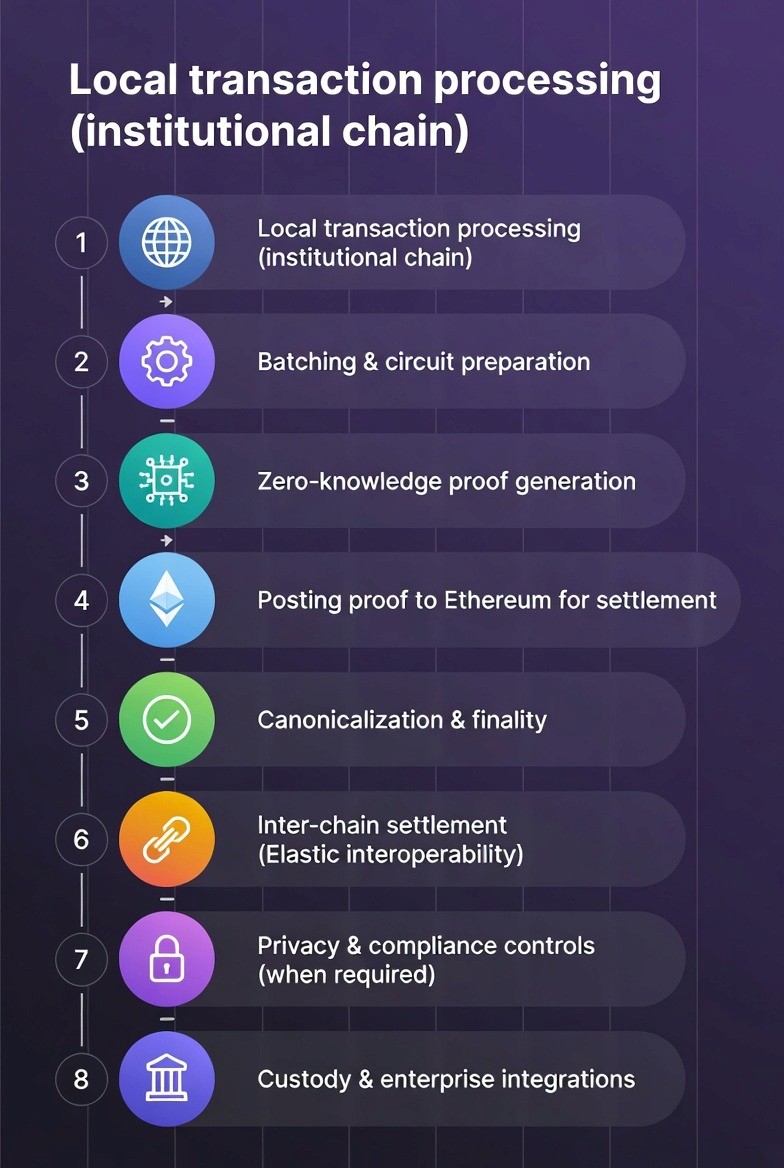
Let’s walk-through an exact sequence of events for a bank or institution making a transaction using the Elastic Network.
Step 1: Transaction Processing Locally
A bank customer makes a transaction on his/her/their organization's elastic chain. For example, a bank customer transfers $1000.00 to the bank's blockchain. The transaction will then be processed by the bank's blockchain using the bank’s defined rules and will be completed immediately.
Step 2: Batching & Circuit Preparation
Unlike creating a proof for a single transaction (which is very costly), the bank will collect 1,000 or 10,000 transactions and bundle them together as a “batch”. Bundling the transactions in a batch is similar to mailing multiple letters in a large envelope rather than mailing each letter separately.
Step 3: Zero-Knowledge Proof Creation
The bank creates a mathematical proof that demonstrates all 1,000 transactions were performed correctly. Due to its smaller size compared to the transactions being bundled, the proof is cost-effective.
Step 4: Posting Proof to Ethereum for Finalization
The bank posts the proof to Ethereum. The computers located on the Ethereum network will review the proof to ensure it is mathematically accurate.
Step 5: Canonicalization & Finality
After Ethereum verifies the proof, the transaction becomes permanent; no one will ever be able to alter it or dispute it. The proof is now officially recorded as part of the blockchain.
Step 6: Inter-Blockchain Settlement (Elastic Interoperability) - Using these proofs, if Bank A's blockchain needs to send money to Bank B's blockchain, the banks do not require a third-party intermediary to facilitate the exchange - the mathematics takes care of the settlement process.
Step 7: Compliance and Privacy Rules at Each Stage
In addition to verifying whether each transaction is valid, compliance rules are also reviewed at each stage to prevent unauthorized transactions from occurring. If a transaction does violate a compliance rule, it will be rejected prior to being included in a batch.
Step 8: Custody & Enterprise Integrations
The system will interface with organizations such as Fireblocks (an enterprise that specializes in managing funds on behalf of institutions).
ZKSYNC ELASTIC NETWORK BENEFITS FOR WEB3 ENTERPRISES
1. Reducing Operating Expenses
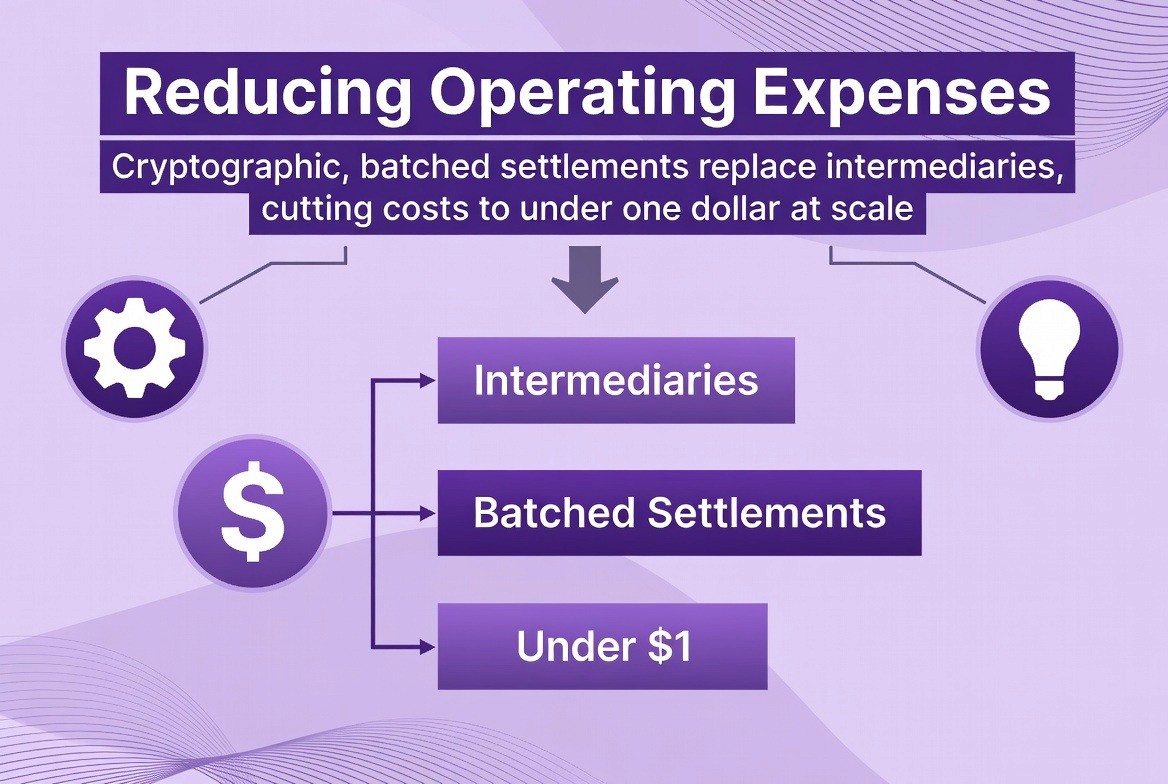
With the Elastic Network, settlement occurs as a result of cryptographic proofs versus third party intermediaries. Settlements are combined into batches and verified via mathematical means; therefore, costs associated with each settlement (which could potentially be over $50 today) will likely be less than $1 at scale. As a result of this cost reduction, there will be long-term cost savings to banks, payment processors, and clearing houses.
2. Enhanced Security

In essence, the Elastic Network takes away this uncertainty. Each settlement is confirmed by a cryptographic proof that shows exactly what occurred. Therefore, it is not necessary to rely on differing accounts or assumptions of trust. When the proof has been verified, then the settlement is accurate. As a result, the number of disputes relating to settlements will be greatly decreased and numerous types of risks related to settlement processes will be eliminated.
3. Increased Auditing Ability
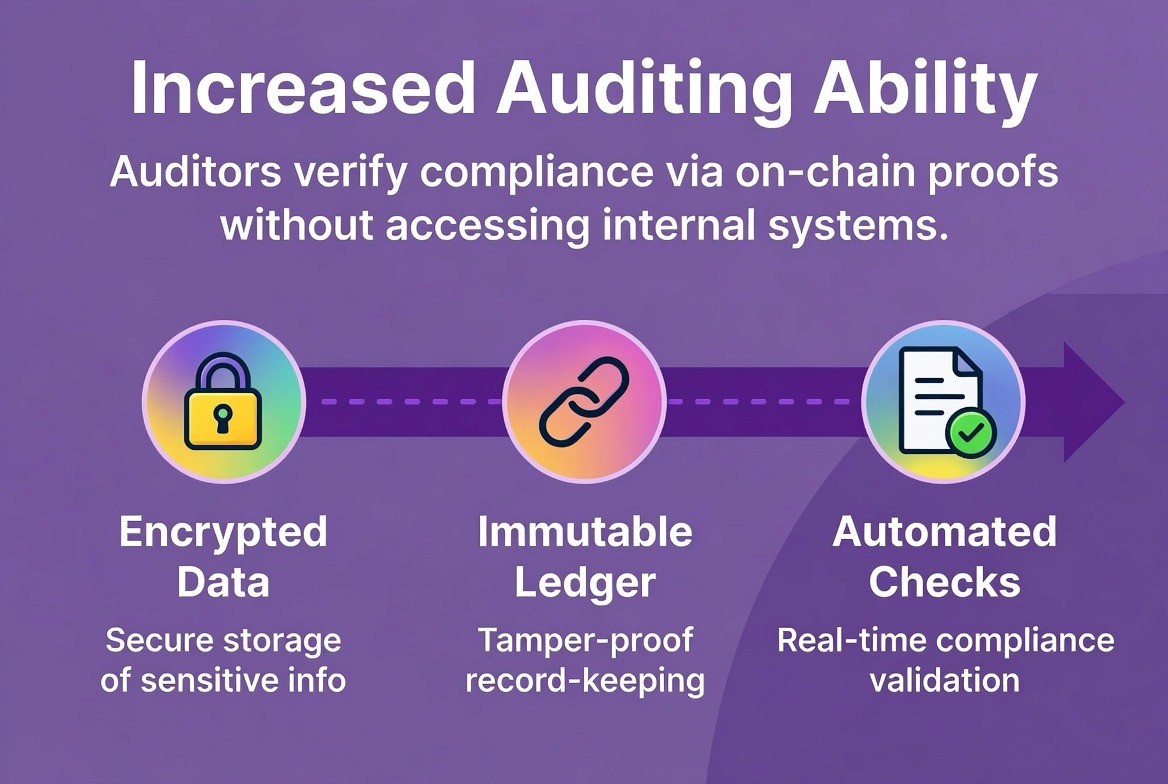
The Elastic Network provides an ability to prove the accuracy of transactions through cryptography. In this manner, regulators may use on-chain proofs to confirm that institutions are complying with regulations without having access to the inner workings of a financial institution’s systems or other sensitive infrastructure. The auditing ability provided by the Elastic Network will make audits easier, shorten audit cycles, and decrease the burdens placed on both institutions and regulatory bodies.
4. Private Self-Sovereign Blockchains
The Elastic Network also provides a method for organizations to operate private self-sovereign blockchain networks. Organizations determine who may participate in the network, what information is available within the network, and how the network will be governed. At the same time, all settlements conducted via the Elastic Network will be protected by the security provided by the Ethereum network. Organizations maintain governance and control over their data without sacrificing the security benefits of operating on a global public blockchain network.
5. Reduced Counterparty Risks

Settlements occur nearly instantly after verification on the Elastic Network. Therefore, the window of opportunity for issues to arise between the time a settlement is initiated and completed is dramatically shortened. Because funds are settled so quickly, there is a much lower likelihood that some type of issue will arise during the settlement process.
Benefit | What This Means |
Lower Operational Costs | Settlements that cost $50 right now could cost less than $1 |
Stronger Security | No more settlement disputes—math proves what actually happened |
Auditability | Regulators can check everything without needing access to secret bank computers |
Private Sovereign Chains | Organizations keep control of their blockchain while getting Ethereum's security |
Reduced Counterparty Risk | Money settles in seconds instead of days, so less can go wrong |
Table of Comparison
Different blockchain and settlement options have different strengths and weaknesses:
Feature | zkSync Elastic | Ethereum Regular | Other Layer-2 | Private Blockchains |
Security | Very high (proven by math) | Highest (most famous) | High (depends on type) | Low (you have to trust them) |
Cost Per Transaction | Less than a penny | $10-200 | A few cents to a dollar | Cheap to run but expensive to set up |
How Fast | Super fast (scales up easily) | Limited (always slow) | Fast (but varies) | Fast (but only for them) |
Privacy | Very private (when you want it) | Totally public | Somewhat private | Completely private |
Works With Other Systems | Yes (easily) | Yes (but it's the main one) | Kind of (lots of confusion) | No (stuck alone) |
Good for Banks | Excellent | Bad (too public and expensive) | Okay (missing privacy) | Good (privacy problem: stuck alone) |
How Hard to Set Up | Medium (tools available) | Easy (everyone does it) | Medium (medium difficulty) | Hard (build everything yourself) |
REAL USE CASES
Here are actual companies using the Elastic Network:
Sygnum Bank
Sygnum is a real bank in Switzerland. They took $50 million and turned it into digital tokens using zkSync. This proved that regular banks think the Elastic Network is safe and trustworthy enough for real money.
Fireblocks
Fireblocks is a company that stores digital money for banks and investment companies. They added zkSync support so their customers (who include major banks) can manage money on the Elastic Network without switching to a different provider.
WonderFi
WonderFi created their own blockchain using the Elastic Network to deliver financial products that are faster and cheaper than traditional products.
Prividium
This is a special version made just for privacy and regulatory compliance. If a company needs maximum privacy and wants to follow every government rule, Prividium is the product they use.
Lens Protocol
Lens Protocol is a decentralized SocialFi network with over 100,000 users that uses zkSync Elastic Chain(s) to scale social applications while preserving decentralization, security, and cross-chain interoperability.
Memento
Memento uses zkSync Elastic Chain(s) to bridge traditional finance and DeFi, enabling secure, scalable, and compliant digital fund management for a potential base of up to 14 million Deutsche Bank customers.
THE ELASTIC NETWORK INTEGRATION PROCESS
To implement the Elastic Network at a bank or other financial entity, there are four general steps to follow;
Phase 1: Define the Settlement Workflow
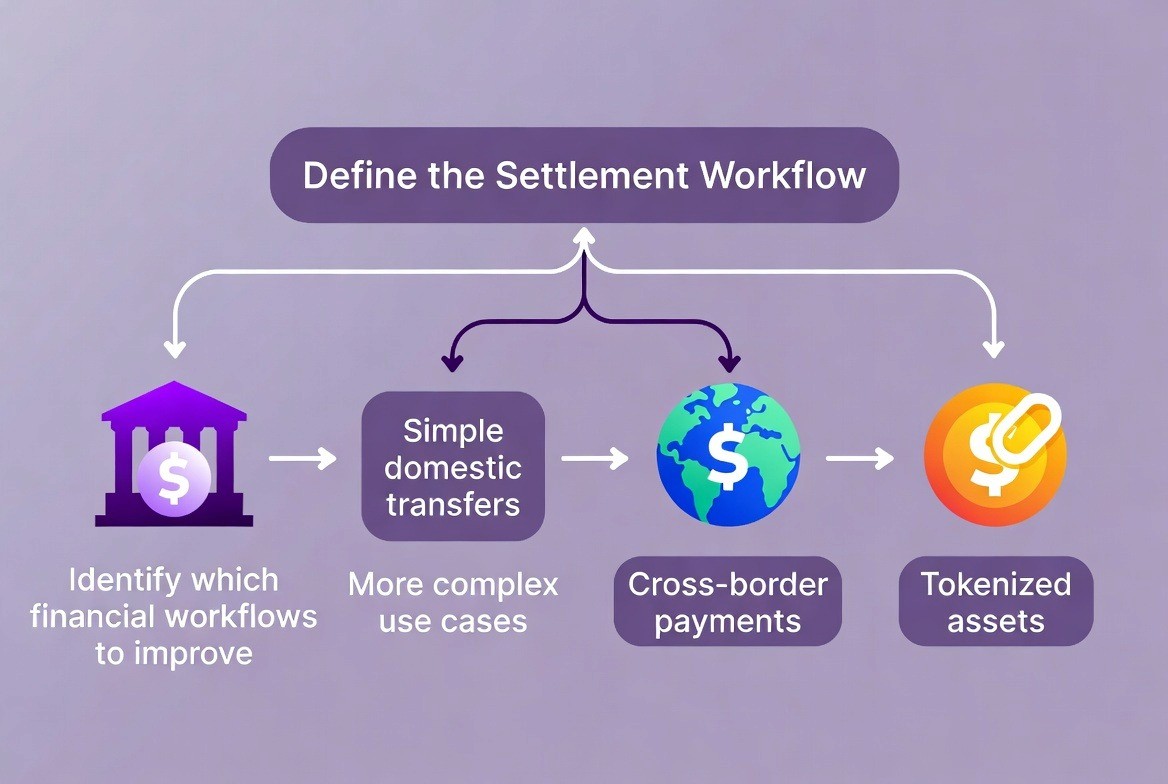
In Phase 1 the organization defines the workflows for the financial activities that will be improved. They may start by improving simple domestic transfer activities and later expand to include international payment transactions as well as the transfer of tokenized assets. They typically take this approach in order to limit exposure to new risks associated with the use of blockchain technology.
Phase 2: Deploying a Blockchain (Chain Deployment)
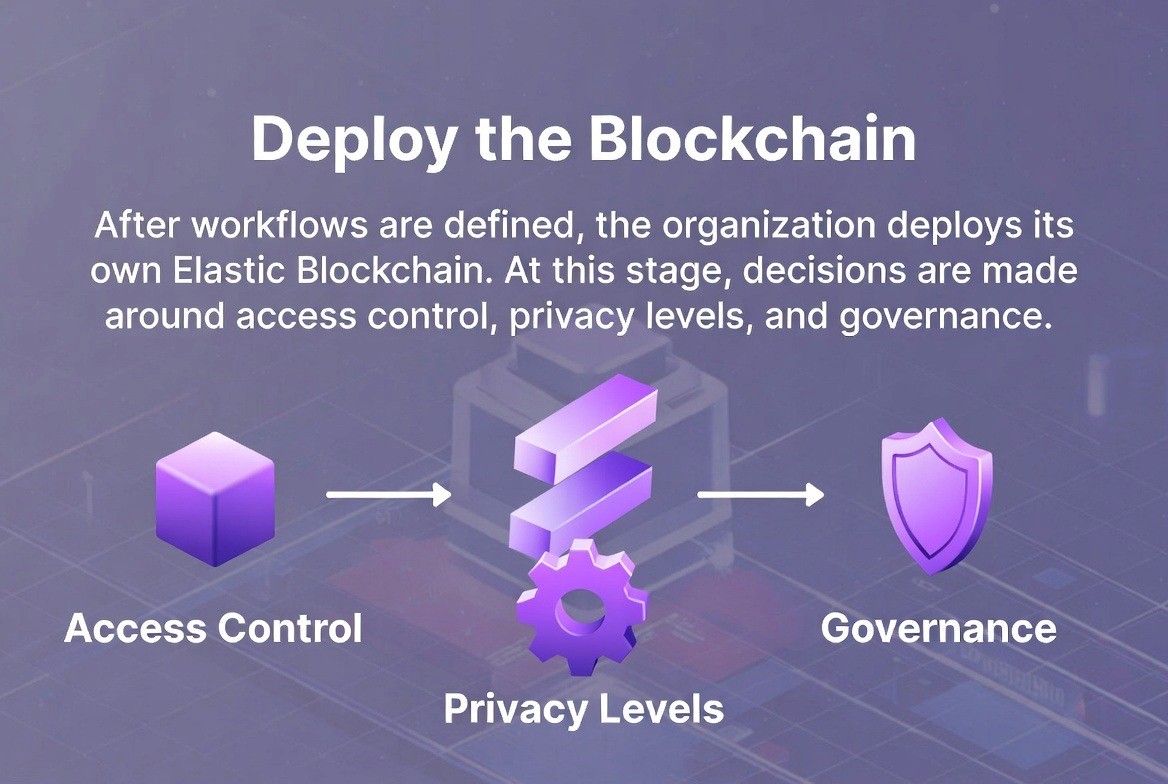
Once the organization has identified the financial workflows to be improved using the Elastic Network, they create their own Elastic Blockchain. Creating a chain requires decisions related to who will have access to the chain, the level of privacy desired, and who will control the workflow.
Phase 3: Integrating Compliance Tools

Once the chain is created, the next step is to integrate compliance tools into the blockchain. The compliance tools will require modifications to accommodate the use of cryptographic proof versus traditional paper based documentation.
Phase 4: Test and Phase Rollout
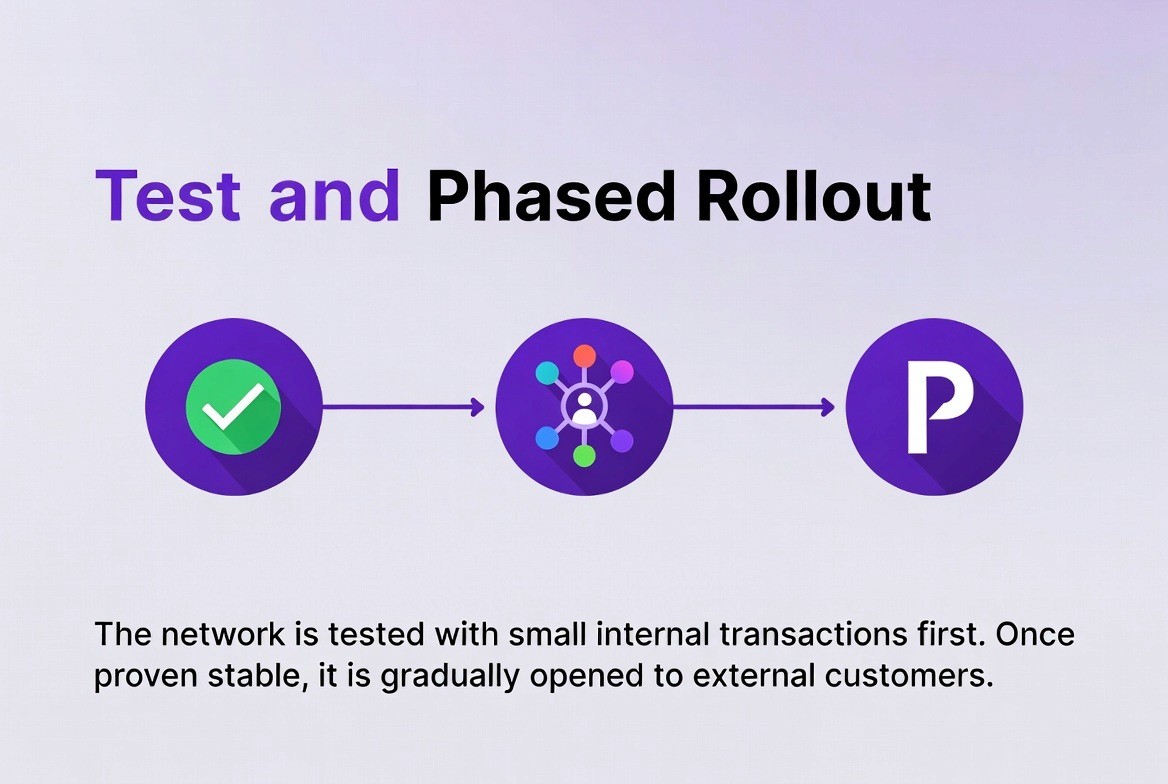
The last phase is to test the functionality of the blockchain network in a phased rollout. This involves testing the functionality first with small amounts of funds (i.e., their internal treasury). Once tested, the organization will allow actual customers to begin using the network.
THE DATA
Let's look at numbers that show why organizations care about the Elastic Network:
1. Tokenization Market Growth
Financial experts predict that by 2030, $10 to $16 trillion worth of assets will be in digital token form. That's a huge market. Right now only $300-400 billion is tokenized, so the market is going to grow massively. The Elastic Network is being built for this huge future market.
2. Institutional Confidence Signals
One study asked 500 investment professionals "Will tokenization change asset management?" 97% said yes. That means almost every professional in finance thinks this is coming. But most are waiting for the right technology (like the Elastic Network) before they jump in.
3. zkSync Elastic Adoption Metrics
Right now 19+ different organizations have launched their own Elastic Chains. This shows it's not just one or two companies—there's real interest across the industry.
4. DeFi Sector Value at Stake
"DeFi" means Decentralized Finance, which is crypto finance without banks. DeFi currently holds about $140 billion. But this money is at risk from hacks and mistakes. Institutions want to use blockchain for the speed and cost benefits, but they want it to be safer. The Elastic Network provides this safety.
5. Blockchain Scalability Breakthroughs
The Elastic Network can handle 15,000 transactions per second. Ethereum normally handles 15 transactions per second. That's 1,000 times faster. Plus, transactions cost 90% less. This is the kind of improvement that makes blockchain practical for banks.
Metric | Number | Why It Matters |
Tokenization market by 2030 | $10-16 trillion | Huge opportunity for settlement technology |
Institutional interest | 97% think tokenization will change finance | Everyone wants to use it when it's ready |
Elastic Chains launched | 19+ | Real organizations are using it |
DeFi assets | ~$140 billion | Big money looking for safer blockchain |
Transaction speed | 15,000 TPS | 1,000x faster than Ethereum |
THE OUTLOOK
The Elastic Network is not positioned as a short-term upgrade, but as a long-term shift in how financial systems settle value. Its direction reflects where both institutions and regulators are already moving: toward infrastructure that combines privacy, transparency, and speed without forcing trade-offs.
Convergence of Public & Private Settlement
Right now organizations use either fully private systems (which nobody can see) or fully public blockchains (which everybody can see). The Elastic Network offers a middle ground. Organizations will increasingly move toward this middle ground because it's the best of both worlds.
Regulatory Alignment
Government regulators are starting to understand zero-knowledge proofs. They realize that cryptographic proofs actually show rule-following better than traditional audits. Over time, regulators will require this technology because it's more reliable.
Global Settlement Mesh
Instead of every bank settling with every other bank through multiple intermediaries, imagine a worldwide network where any organization can settle with any other organization instantly. The Elastic Network makes this possible.
Sovereign-Grade Infrastructure
Countries and central banks are starting to care about this technology. Some governments are building digital versions of their currency, and they want to use the Elastic Network for this. This is huge because when governments adopt something, you know it's here to stay.
FAQ
1. What is the zkSync Elastic Network?
The zkSync Elastic Network is a blockchain settlement system designed for banks and regulated institutions that allows each organization to run its own customized blockchain while using Ethereum as the final, secure settlement layer.
2. How is the Elastic Network different from a traditional blockchain?
Unlike traditional blockchains that force all users to follow the same public rules, the Elastic Network allows organizations to configure privacy, governance, and compliance rules specific to their regulatory and business needs.
3. Why can’t banks use Ethereum directly for settlement?
Ethereum is highly secure but fully public and often expensive, making it unsuitable for sensitive financial transactions that require confidentiality, regulatory controls, and predictable costs.
4. How does the Elastic Network support regulatory compliance?
Compliance rules can be built directly into the blockchain so that non-compliant transactions are automatically rejected, ensuring regulations are enforced by the system rather than by manual oversight.
5. What is a zero-knowledge proof in simple terms?
A zero-knowledge proof allows an organization to prove that a transaction followed all rules without revealing sensitive details such as identities, balances, or transaction amounts.
HOW TOKENMINDS HELPS WITH ELASTIC NETWORK DEPLOYMENT
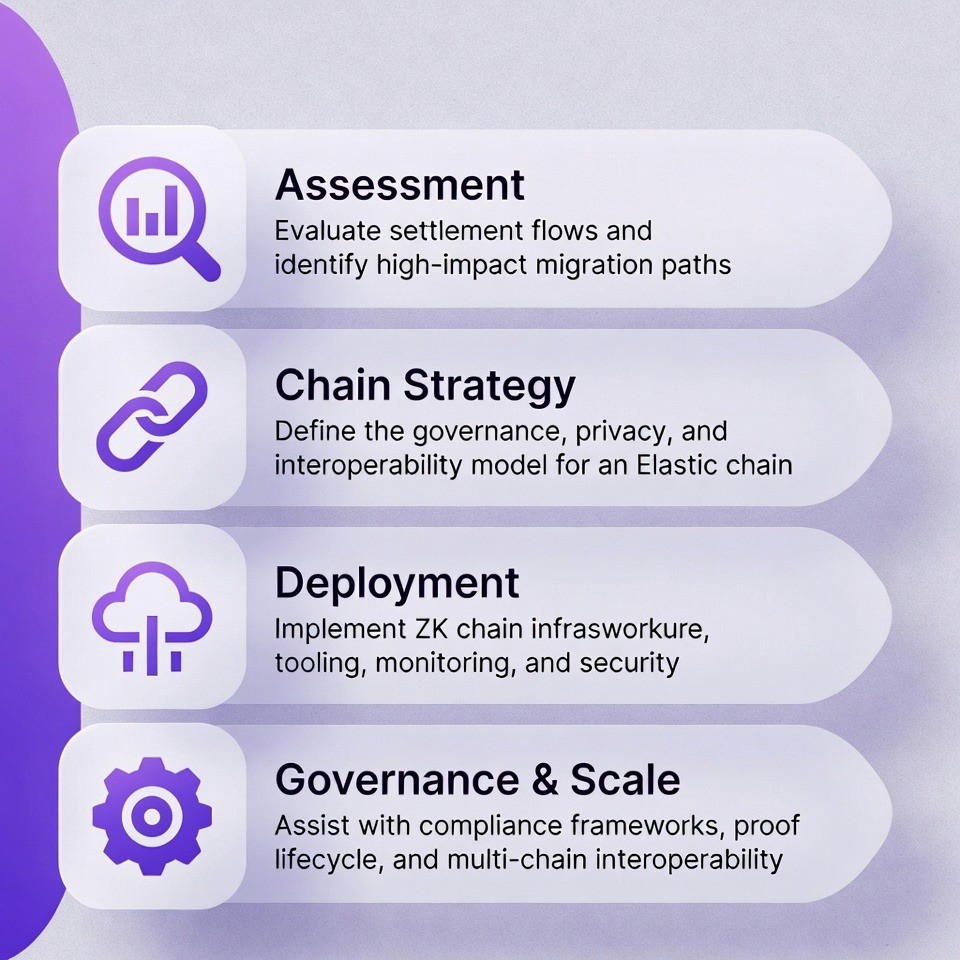
Organizations exploring the Elastic Network often find that implementation raises practical and architectural questions. TokenMinds works with teams to help them understand the technology and apply it in a way that fits their operational and regulatory context.
Assessment: TokenMinds looks at how an organization currently moves money and finds where the Elastic Network would help most. They find the biggest problems and explain how the Elastic Network solves them.
Chain Strategy: They help the organization decide what their blockchain should look like. Public or private? How many organizations run it? What assets can be traded? These are big decisions that need expert guidance.
Deployment: TokenMinds helps actually build and launch the blockchain. They set up the technology, make sure it's secure, and connect it to the organization's existing systems.
Governance & Scale: As the blockchain grows, governance gets more complicated. TokenMinds helps manage this. They help write the rules for how the blockchain makes decisions, how it changes over time, and how it connects to other blockchains.
CONCLUSION
The zkSync Elastic Network is a major breakthrough in how technology can help finance work better. It solves the main problems that stopped banks and large institutions from using blockchain: the need for privacy, the requirement to follow government rules, and the need to know for sure that transactions are final. For the first time, organizations can use blockchain technology without sacrificing privacy or regulatory compliance.
Schedule a complimentary consultation with TokenMinds to explore how the Elastic Network can be integrated into your platform’s settlement and transaction flows, enhancing privacy, security, and interoperability while fitting smoothly into your existing systems.








