TL:DR
How to enable efficient, scalable bancassurance by using AI to automate underwriting, fraud detection, and hyper-personalized product recommendations, while blockchain smart contracts eliminate reconciliation delays and execute insurance policy terms without manual intervention.
Manual coordination of systems among banks and insurance companies causes bancassurance platforms to lose money and customer trust, while data is duplicated, reconciliations take a long time to complete, and claims are processed slowly and inaccurately. Blockchain and AI for bancassurance can solve these problems by making automated decisions, removing delays from reconciliations, and enabling the execution of transactions in trusted, shared infrastructure.
Core Problem in Bancassurance
Bancassurance refers to the marketing and distribution of insurance products through banks' operating channels. In general, each bank and insurance company operates independently from other banks and/or insurance companies using their own individual technology systems. Thus, a bank’s customers’ personal identifiable information (e.g., name, address), as well as their insurance-related product history (i.e., policies sold, premiums paid) and all transactions related thereto (e.g., payment history) reside in separate database, a fragmentation created by independently developed blockchain-based systems.
When a bank sells an insurance product to one of its bank customers, it is necessary for the bank to manually transfer the customer’s data to the relevant insurance company’s computerized underwriting system. As such, duplicate entries may occur, versions of the same document/data will conflict with each other, and a delay will likely exist prior to processing.
In order to process an underwriter’s decision regarding an insurance application, there must be a two-way (back-and-forth) communication between both systems and personnel. The claims adjudication process also includes multiple manual validations that can take anywhere from a few days up to several weeks.
The resultant is; (1) very high operational costs associated with the bancassurance process, (2) very long times to deliver service to the bancassurance customer, and (3) a very poor customer experience when dealing with the bancassurance process. Fraudulent activity is detected on a “reactive” basis and not on a “predictive” basis. Opportunities to cross-sell additional insurance products to existing customers are lost because no real-time sharing of customer knowledge/insight occurs.
Business Impact of Fixing Bancassurance Inefficiency

Banks lose potential revenue because they miss opportunities to sell insurance products as customers experience changes in their financial status, (e.g. receiving a raise in salary or taking out a mortgage). These are obviously good times to offer either life insurance or property insurance. Absent from AI-based marketing systems, these opportunities go unexploited.
Manual processing and reconciliations create high costs to deliver each new policy. The human involvement required in reviewing each application, entering information into systems, and completing approval workflow processes limit how many applications an individual can process, thereby increasing the total labor expense to complete those applications.
The time it takes to settle a claim damages a bank's relationship with its customers. When a customer has a claim, and there is a two-week delay before it is settled, it generates dissatisfaction, and will likely cause them to leave the bank. Customers have come to expect that all banking services will be delivered through digital means, and therefore, should occur at the same level of speed and convenience as internet banking.
Automated systems, which utilize AI technology for predictive targeting and immediate underwriting capabilities, decrease the cost per transaction, increase the number of policies sold, and increase profitability. Technology utilizing AI for insurance, and blockchain for insurance, enable enforcement of policy terms and automatic settlement of claims without human intervention.
AI in Modern Bancassurance
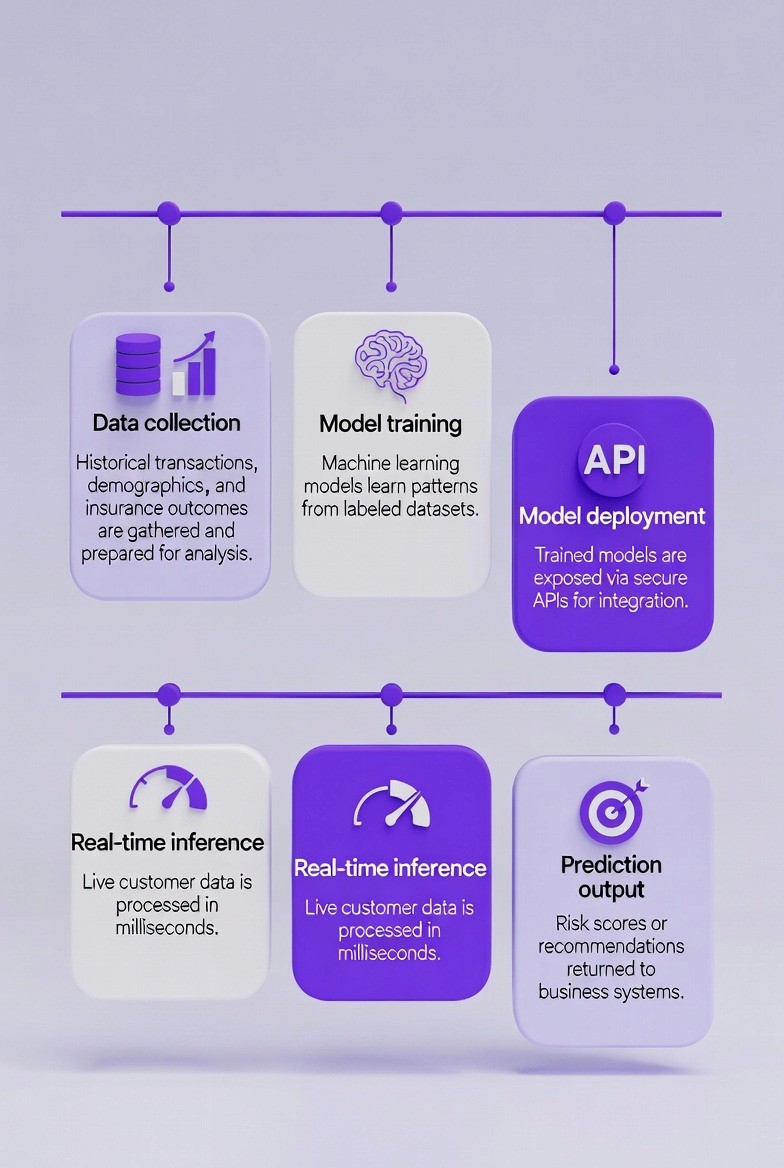
Bancassurance is a large-scale business which serves millions of customers and performs thousands of transactions every single day. Therefore manual reviews cannot possibly keep up with the amount of transactions; similarly, human analysts cannot analyze customer information quickly enough in order to find opportunities in a timely manner.
Therefore, AI (which utilizes machine learning algorithms) is used to train models based upon historical customer data so that it can predict customer behavior, assess customer risk, and provide product recommendations. The AI models analyze patterns within banking transactions, demographic data, and external data sources, a process increasingly driven by AI engines purpose-built for bancassurance decisions like this workflows. Additionally, AI can operate continuously and improve its ability to make predictions based upon an increased amount of customer data.
AI also significantly decreases decision making times from days to seconds. Previously, underwriting had to be manually reviewed by humans for low risk policies, however; this has been replaced by automated processes utilizing AI. In addition, claims can be validated immediately if all predetermined conditions have been satisfied.
AI Integration in Bancassurance: Key Benefits
1. Hyper-Personalized Marketing and Sales
Bank transaction data is analyzed by AI to determine salary deposits, regular bill payments, merchants, etc., along with withdrawal history. Life event changes are also detected (marriage, birth of children, purchase of a home, opening a business). These changes will indicate an individual's insurance needs.
An example would be a customer that starts paying school fees, the customer most likely has children; they probably require either education or life insurance. A customer who just recently made their first mortgage payment will require property and liability insurance. The AI system produces all of this automatically and sends a product offer to customers via the banks' digital channels at the time the offer is most suitable for them.
All forms of generic mass marketing are eliminated. Customers receive personalized offers from the bank, specific to each customer's financial information and/or circumstances of the customer at any given time. As a result, conversion increases because offers match the customer's true needs.
2. AI Agents for Service and Sales
AI Agents are digital assistants that use large language models (LLMs). LLMs are an area of AI where the model is trained on vast amounts of human language in order to be able to both understand and generate human language. As such, AI Agents function as virtual colleagues for customers' inquiries, providing them with policy information and generating insurance quotes.
Customer interaction occurs via mobile banking Apps, WhatsApp, website, or voice calls. AI Agents answer customer inquiries about their various coverage options, explain policy terms and complete insurance applications for the customer. They operate 24/7 with no wait time for customers.
Additionally, AI Agents support human sales teams. The AI Agent assists the sales team by suggesting the next best action for the sales representative, retrieves the customer's history and assists with drafting policy documents. Through this assistance, productivity has increased and consistent service levels have been maintained for the sales teams.
3. Intelligent Lead Scoring and Management
AI evaluates the likelihood of potential customers purchasing insurance by analyzing their financial information; past purchase history (i.e., transactions); and their likely need for an insurance product. The AI assigns each lead a number that represents how likely it is to convert that lead into a sale. Leads that have both a high value and are high in urgency are given priority for immediate follow-up from the sales team.
Example of high-scoring lead: A person whose income is increasing and has been steadily employed without currently owning any life insurance will be assigned a high score. Example of low-scoring lead: A person who has had an inconsistent stream of cash and recently purchased another insurance policy will be assigned a lower score. The sales teams can therefore focus their efforts where they can earn the most revenue.
The use of AI to evaluate potential customers reduces the amount of time salespeople spend evaluating leads that do not appear likely to result in a sale. Additionally, the use of AI results in customers with urgent needs being contacted sooner than those with less urgent needs.
4. Streamlined Underwriting and Claims
Automated risk assessments through machine learning reduce the amount of time required to complete the underwriting process for standardized policy types. The AI model evaluates all customer information (credit history, medical questionnaire information, etc.), as well as transactions to generate a risk classification and corresponding premium recommendation within seconds.
Industry implementations have shown a reduction in time for underwriting standard term life insurance policies from 3 days to 2 minutes. In addition to the improvement in time, approval rates are improved when using an automated system; this is true because while there may be some risks identified by the AI that would be rejected by a human underwriter due to the lack of time to review the application thoroughly, the AI will find risks that the human underwriter missed or did not see based on the limited amount of time available to review the application.
Automated systems also detect potential fraud in the claims process. They flag discrepancies in documentation submitted with claims; they identify when claims are duplicated; they compare claim patterns against existing records of fraudulent activity. These capabilities result in fewer payment errors being made and prevent fraudulent claims from being paid prior to further investigation into those claims.
5. Real-time Customer Support and Compliance
AI analyzes real-time customer interactions (calls, chats) to provide live support to human representatives in that conversation. The system will identify what is being asked (question), whether there are any regulatory issues associated with that question, and what the best answer should be; all in an effort to guide the representative through a call or chat while they follow their script and comply with company regulations as much as possible.
Additionally, AI can monitor how the customer feels about the interaction (sentiment), and if the customer indicates they are unhappy with the service they have received, AI can flag this issue and escalate it to someone who has the authority to assist the customer further. AI can also create a summary of the conversation after it is completed, so that both the representative and supervisor/quality team member can view the details of the call/chat for training and/or auditing purposes. By utilizing these functions, companies can increase consistency in providing quality service, while decreasing the number of compliance issues.
How to Integrate AI into Legacy Bancassurance Systems
Data ingestion from core banking and insurance systems. Extract customer profiles, transaction histories, policy records, and claims data. Use batch file transfers or API connections to consolidate data into a centralized data warehouse or data lake.
Data normalization and customer profile creation. Clean, standardize, and merge data from different sources. Create unified customer profiles that combine banking and insurance information. Resolve duplicate records and missing fields.
Model training and deployment. Train models to predict lead scores, determine how much credit risk a customer represents, whether an account is likely fraudulent, and whether or not a customer will leave your bank by analyzing historical data. Validate your model's performance using test sets and use source control for your production model deployments.
AI decision engine integration via APIs. Build API endpoints that accept customer data and return predictions, recommendations, or risk scores. Integrate these APIs into banking applications, CRM systems, and insurance platforms. Ensure low latency for real-time decisions.
Channel integration for CRM, mobile apps, and messaging platforms. Integrate the channels of your organization (e.g., CRM, Mobile Apps, Messaging Platforms) so that you can connect artificial intelligence agents to the customer facing channels (e.g., mobile banking app, WhatsApp, Website Chatbots, Call Center Systems) in which customers interact with your company. Create the capability for Natural Language Understanding and Multi-Turn Conversations within those agent interactions.
Monitoring, retraining, and governance. Keep track of your model's performance through metrics such as Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and Processing Time. As you obtain new data, the models should be retrained and Governance Controls implemented to ensure Fairness, Transparency, and Compliance with Regulations.
Blockchain in Bancassurance
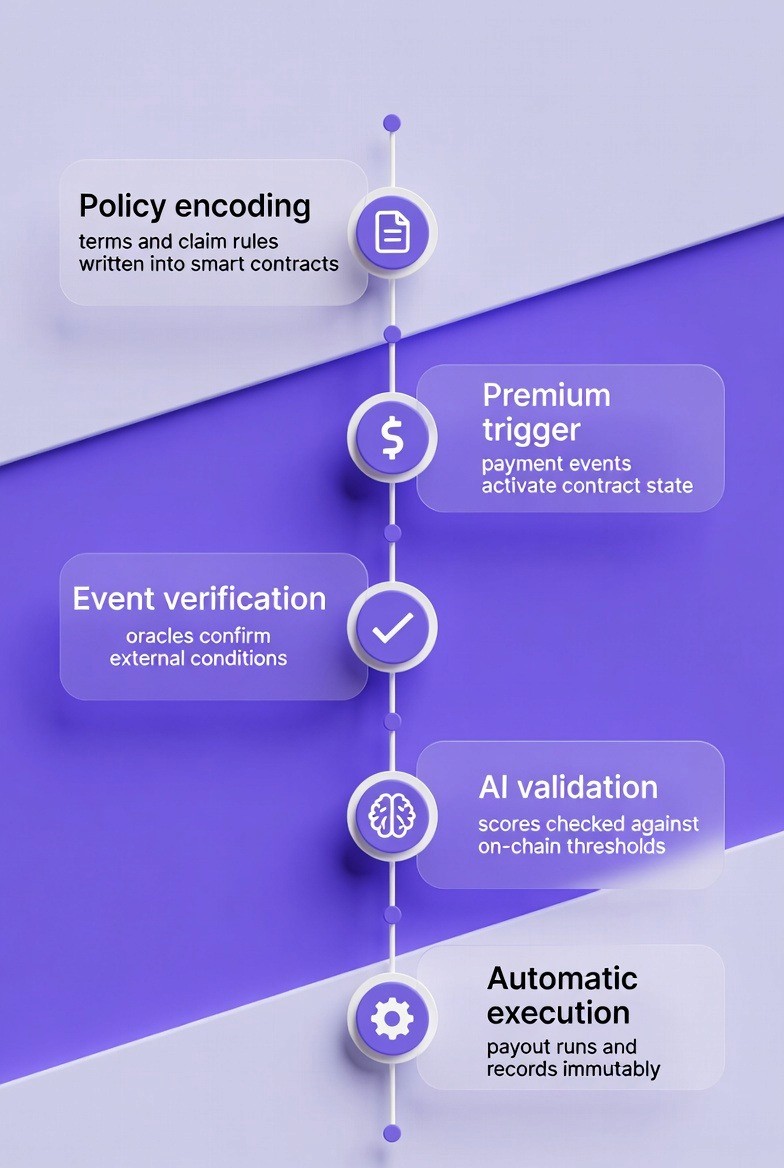
Blockchain offers a shared, tamper-proof ledger for both banks and insurers to use. In order to work together, there has to be trust among them. The reason there has to be trust is because of the need for policy terms to be enforced in the same manner as premium payments are made and claims are paid for, without disputes arising.
Manual enforcement would require all parties to rely on contracts, emails, and meetings for reconciliation purposes.
Blockchain allows for automated enforcement by means of smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing programs that are stored on a blockchain. When specific predetermined conditions have been met, a smart contract will perform a certain action or set of actions. As an example, a smart contract could release a claim payout when a flight delay exceeds three hours.
There is no longer a need for both parties to reconcile their own versions of the records as the shared record is permanent and cannot be changed at a later date. All parties see the same policy information, premium payment history, and claim status.
Blockchain Integration in Bancassurance – Key Benefits
1. Single Source of Truth for Policies
The blockchain contains all policy documents and these are stored in a permanent ledger. Permanent refers to the fact that once data is recorded on the blockchain it can never be modified or erased. As a result both the Bank and Insurer have identical ledgers for their records.
Each time a new policy is issued the smart contract records the policy number, coverage amount, payment (premium) schedule and the name of the beneficiary. Each subsequent alteration, i.e. an endorsement, cancellation etc., is recorded as a separate entry on the smart contract. This process results in a full, transparent record of events.
Both parties will eliminate disputes over what the policy covers and/or the terms of the policy since they will both be referencing the same document. Since there is no need to synchronize the data, this synchronization occurs automatically and instantly.
2. Smart Contract Automation
Automating policy issuance through smart contracts relies on a contractual agreement (policy) that is generated after verifying customer data; the premium has been paid; and the risk of the customer/insured has been approved. Upon the completion of all these conditions the smart contract generates a policy record and creates a unique policy number which does not require any manual approval.
The smart contract also automates the enforcement of premiums through scheduled reviews of whether the premium payment was made on or before the due date. Once the smart contract determines that a premium payment has not been made on time it automatically changes the policy status to "lapsed" and sends notifications to both the insurer and insured regarding the lapse in coverage.
Smart contracts also automate claims processing based upon predefined policies. For instance, a smart contract for travel insurance will process a claim for a flight delay based upon receipt of a flight status update from an oracle (an external source of information). As previously mentioned, an oracle is a service that feeds data about off-blockchain events onto a blockchain so that a smart contract can access and use that information. After receiving a flight status update from an oracle the smart contract validates whether the flight was delayed long enough to be eligible for payment under the terms of the policy, and then pays out automatically.
This eliminates manual approval steps and reduces settlement time from days to minutes.
3. Faster Claims and Settlement
Traditional ways of filing claims are very manual and typically involve paperwork that is submitted and manually reviewed by some type of person or people. After that, there will be an investigation into potential fraud before approvals are made and funds are paid to claimants. Each step in the manual process takes time which makes the entire process lengthy and time consuming. On the other hand, using a Blockchain could automate all or part of the manual steps listed above; however, it will only do so if the automated process has previously established parameters that are required to be met before the process is automatically initiated.
Parametric type insurance allows for immediate payment when there has been a measurable event. An example would be earthquake magnitude or rainfall levels. Once the event occurs, an oracle provides the smart contract with the event data. If the smart contract finds that the parameter has been exceeded, it will execute the payment immediately.
Indemnity-based claims use artificial intelligence to validate the documentation submitted by the claimant and then submit that validation to the blockchain. The smart contract then analyzes the results of that validation and executes payment if the validation score indicates that the claimant was not fraudulent, and therefore the score is below the established thresholds.
4. Auditability and Compliance
Blockchain keeps an exact record of all transactions (and other events) that have occurred (including policy changes or claims), and each of those events is time-stamped and signed electronically. The regulatory body can look at the blockchain ledger in order to verify if an institution has complied with the regulatory requirements rather than asking for information directly from the institution.
The audit trail is complete and unalterable. Auditors will be able to track the entire history of any policy from the date it was issued until it was settled through a claim. As such, regulatory reporting becomes simpler; therefore, the cost of regulatory compliance is reduced.
How to Integrate Blockchain into Legacy Bancassurance Systems
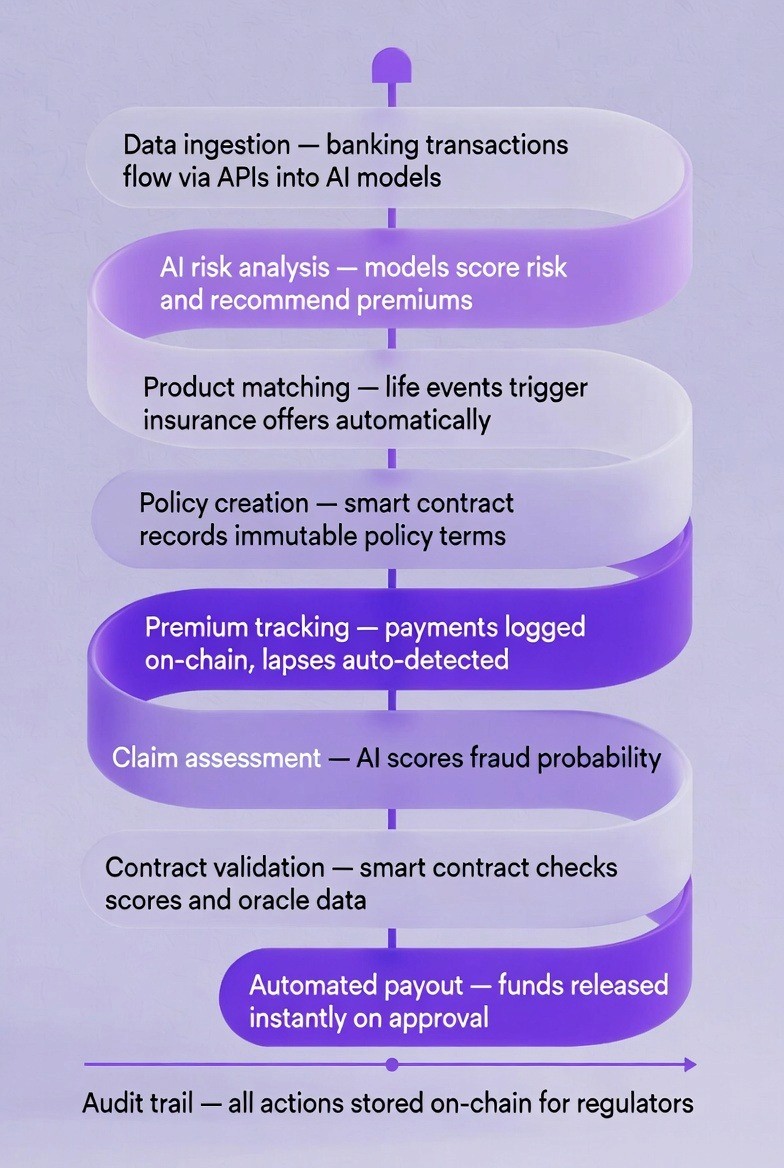
1. Define shared data models for policies and claims
Develop shared data models for policy and claim data across parties. The model must be consistent in field name, data type and validation across all partners. Each partner should document their own field mapping as well as any required transformations when transferring data from one system to another.
2. Deploy permissioned blockchain network
Create a private Blockchain environment. Create a blockchain that only the banks and insurance companies participating in the program will be able to use. This may be accomplished through the use of a platform like Hyperledger Fabric, or an Ethereum based network with permissions. Determine which nodes are in your environment; decide how the nodes will reach consensus on the state of the network; determine who has access to view and write to the environment, as defined by this structured blockchain development approach for enterprise systems.
3. Develop smart contracts for policy and claims logic
Create smart contracts that implement the policy and claims business logic. Develop smart contract code using programming languages such as Solidity or Chaincode. Include features for creating policies, tracking premiums, submitting claims, validating claims, and disbursing payouts. Test the smart contracts on a development network prior to deploying them into production.
4. Integrate oracles and event data sources
Connect with third party oracles and data suppliers to collect event data for use in making decisions within your smart contract. Determine what type(s) of data you need to use to make a decision in your smart contract, and then connect with a third party supplier for this data (e.g., a payment gateway, an IoT sensor, a weather service, a flight tracking system). Use oracle code to query the third party APIs for the required data and input that data into your smart contract. Verify that all data is both complete and trusted.
5. Connect blockchain to banking and insurance systems via APIs
Implement APIs for connecting the Blockchain to the Banking and Insurance Systems. Create an intermediate layer that would convert all of the core banking system requests into blockchain transactions. Permit these systems to check the status of the blockchain currently, ask for the generation of new blockchain transactions and send notifications when there are changes made to the blockchain. Implement a means for managing/ recovering transaction failures by using retry logic and error handling.
6. Enable reporting, audit, and access control
Create reports to enable auditing and reporting features for users; Establish an audit trail to report changes made by administrators and users as well as provide a record of all changes made to the system and transactions completed. Provide a dashboard view to allow administrators and regulatory officials to review the history of all claims submitted and the current status of all active policies. Determine which roles will have read-only access to certain data in order to meet auditing requirements for regulatory purposes. Determine what roles are required to complete and submit new transaction requests. Determine what roles are required to update smart contract logic.
How AI and Blockchain Work Together in Bancassurance
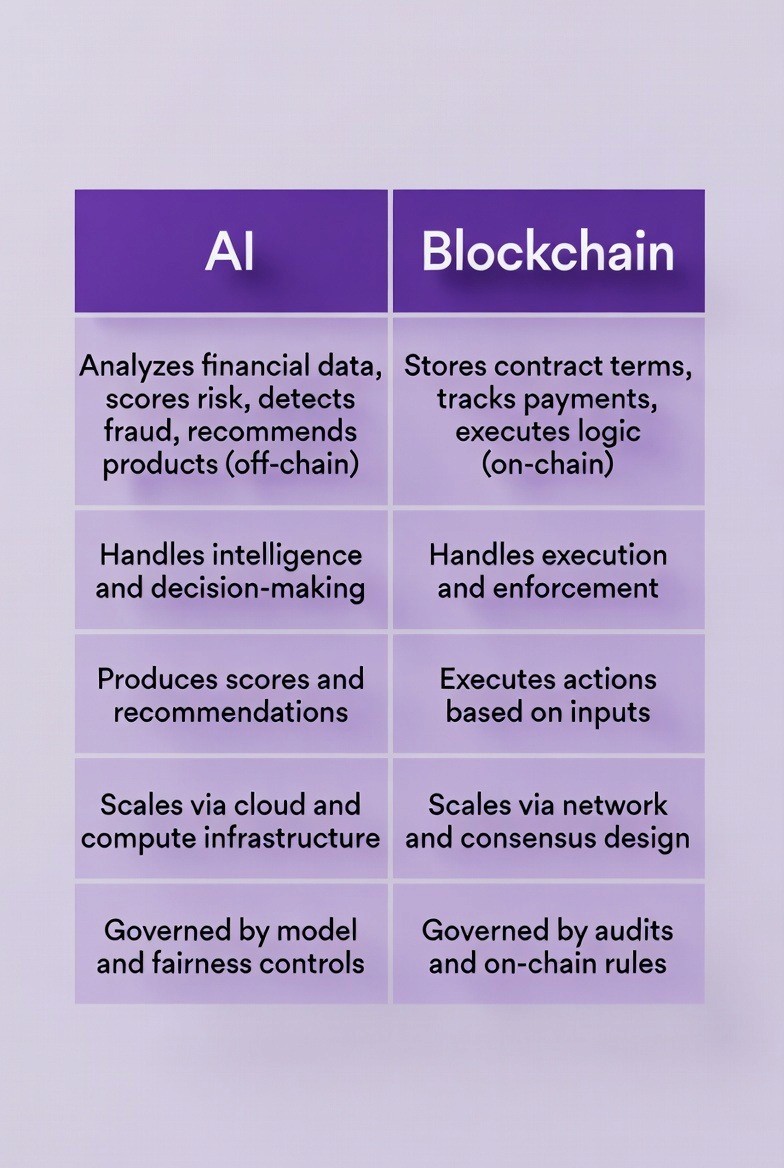
AI uses the analysis of customer data to make recommendations and predictions and thus to determine what insurance needs a customer has and then to provide product options and a level of risk associated with that product and to detect fraudulent activity, etc. AI can be considered "off-chain" or a part of a centralized system where there is ample processing capacity and access to data.
Blockchain enforces the rules by executing the outcome from an AI decision, and it houses all policy terms, tracks all premium payments, verifies each claim, and releases all applicable payouts. Blockchain functions as a distributed ledger where maintaining data integrity and building trust are paramount.
This separation is required due to the fact that AI requires the ability to frequently update models using a large amount of data; whereas, Blockchain focuses on ensuring that data is executed correctly and accurately.
AI outputs provide input to blockchain smart contracts in order to execute the decision made by AI.
As an example, AI assesses a customer's financial situation and provides a recommendation for a life insurance policy including a specific level of coverage and premium. That recommendation is provided to a smart contract that will create the policy record on the blockchain. AI also evaluates a customer's claim submission and assigns a fraud risk score. That score is received by the smart contract and only if the fraud risk score is less than the fraud threshold does the smart contract release payment.
End-to-End Technical Flow
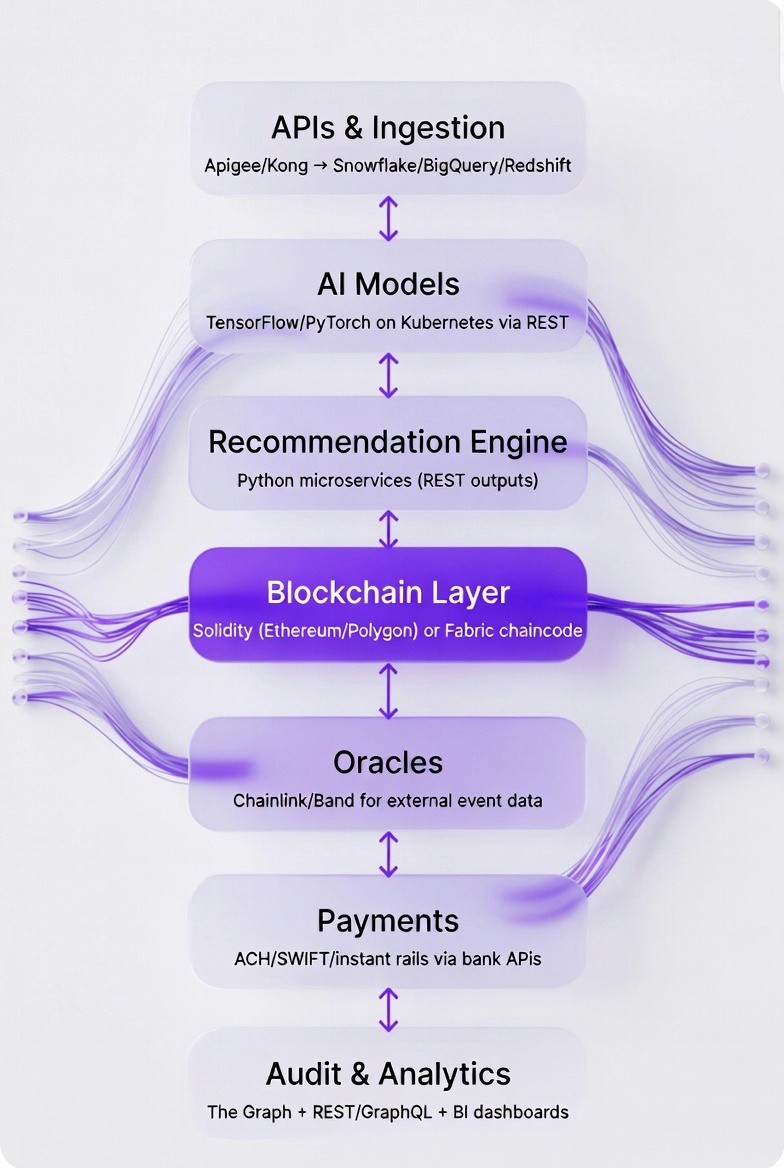
The full technical flow integrates AI and blockchain across the bancassurance lifecycle.
Data ingestion and AI analysis
Transaction data from customers is extracted by API or batch files from core banking systems. Once this data has been collected, it is then loaded into a data warehouse, which is processed by machine learning (AI) models that analyze spending habits, income stability, and life events to provide the customer with an appropriate risk score and/or insurance product recommendation.
Risk scoring and product recommendation
The AI risk scoring model evaluates the customer's credit history, employment status, age, and health indicators. It outputs a risk classification such as low, medium, or high. The recommendation engine selects suitable insurance products and calculates premium amounts based on the risk score.
Smart contract policy creation
The Banking App requests Blockchain Approval via the Banking Apps' API for the Insurance Offer.The Smart Contract receives the information of the Policy (amount of coverage, premium payment schedule, Beneficiary Information and Risk Classification).Smart Contract verifies all received information once this is done. Once the Smart Contract has confirmed that the data was correct, it inserts a New Entry into the Ledger of the Blockchain with an Unique ID for the Newly Created Policy.Both Bank and Insurer are notified that a New Policy Has Been Issued.
Premium tracking
In addition to being able to listen for events that may indicate a change to the status of the banking systems' payment of premiums by the smart contract, it is also notified when each premium is recorded in the blockchain as a transaction that includes a date stamp. When the scheduled premium payments are missed, the smart contract automatically changes the status of the policy to lapsed and sends a notification to both the customer and the insurer.
Claim event detection
An external event occurs such as a hospitalization, flight delay, or property damage. The customer submits a claim through the mobile banking app or insurer portal. The claim details are sent to the blockchain along with supporting documentation.
AI fraud assessment
The fraud claim is sent to an artificial intelligence (AI) fraud model. This model evaluates the fraud pattern based on previous fraud claims, fraud claims by the customer, and document discrepancies. This fraud model provides a fraud claim probability score of a number between 0 and 1. Claims that have fraud scores greater than 0.7 will be reviewed manually by someone.
Smart contract claim validation
A fraud claim score is entered into a smart contract by means of an oracle. The smart contract will then determine if the fraud claim score is below the fraud claim score established within the policy's terms. In addition to fraud claim scores, parametric claims involve querying third party data providers (weather APIs or flight status databases for example) through an oracle to obtain additional information on the claimant's loss. Once all required parameters are met, the smart contract will pay the claim.
Automated payout and settlement
The smart contract makes a payout by telling the bank's payment system to transfer funds from the insurer to the insured customer's bank account. The payout details (the amount of the payout, the date/time the payout was processed, etc.) are recorded on the blockchain so that there is a permanent record of the payout in addition to all parties having immediate access to all payout data on the blockchain.
Ledger update and audit
All information regarding policy changes, premium payments, claims, and payouts are stored on the immutable blockchain. Regulatory bodies and auditors may request data from the blockchain to confirm compliance, track policy life cycles and view history of claims. Since all information is stored on an immutable blockchain there will be no disputes regarding who made what payment or to whom, and this will greatly reduce time required for regulators to collect information needed for reports.
This flow combines AI models and APIs for decision-making with smart contracts, blockchain networks, oracles, and event triggers for execution and record-keeping.
Below is the same content rewritten so a 9th-grade student could understand it, while still sounding professional and credible to business leaders. The logic, structure, and seriousness are preserved—only the language is simplified and clarified.
Launching an AI and blockchain–enabled bancassurance initiative starts with getting the basics right, not with complex technology. Banks and insurers must first align on business goals, data responsibilities, and regulatory boundaries before automation can deliver real value.
Real Live Use Cases

LEMONADE (AI-POWERED INSURANCE)
Company: Lemonade Inc. (NYSE: LMND)
Technology: AI chatbots, machine learning models, telematics
Status: Active production system serving millions of customers
What They Do:
97% of policies are sold through AI bots. 55% of all claims processing is done by AI.
AI algorithms scan large databases looking for patterns or anomalies that could be indicative of fraud
Underwriting models are now using telematics and real-time data to improve the gross loss ratio to 67% in Q2 2025 — an improvement of 12 points from last year
Impact on Business:
Projected revenue from $430 million (2023) to $710-715 million (2025)
As of Q2 2025 in-force premium is $1.083 billion
Underwriting time has gone from days to secondsBlockchain Component:
- Lemonade Foundation launched climate insurance as a stablecoin-denominated decentralized application on the Avalanche blockchain for farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Using blockchain for parametric crop insurance, with immediate mobile payment.
HOW TOKENMINDS HELPS WITH BLOCKCHAIN & AI INTEGRATION
For a bank, TokenMinds takes what you have in terms of customer information and how they interact with you digitally and turns it into a scalable insurance distribution platform. In this way, we will create the bancassurance architecture, provide API connectivity to your core banking systems so as to allow insurers to access them securely, and build AI-based models that identify those customers who would be appropriate to receive an offer of an insurance product within your mobile app, and also enable automation of the underwriting process for lower risk applications. This will allow banks to launch new insurance products quickly and at minimal cost while increasing their fee income, and eliminating much of the need for manual communication with insurers.
For an insurer, TokenMinds can assist in making all or most aspects of the insurance process (i.e., underwriting, issuing policies, paying claims) more efficient by employing AI and blockchain technology. We will develop AI-based tools for assessing risk and detecting fraudulent activity; and we will develop and deploy smart contract functionality on a blockchain to automate the management of all policy-related data including policy records, premium payments, and claim payouts, with complete audibility. This will allow insurers to significantly lower their operating costs, shorten the time to settle claims from weeks to minutes, and seamlessly link with numerous banking partners via a single technology platform.
Conclusion
Bancassurance has historically struggled to scale due to the inefficiencies of disparate systems and manual processes in underwriting, claims and customer service which increases costs and decreases customer satisfaction. Using both blockchain and AI, banks and insurers are able to provide an automatic decision making process; create a system for the real time exchange of data; and automatically execute processes at the same rate and level of consistency as they are executed. AI is used to improve risk assessments, identify potential fraudulent activity and to match customers with products; while Blockchain will provide a trusted platform for data integrity and the automation of execution processes. The combination of blockchain and AI will transform the bancassurance model from an inefficient channel of organic growth into an efficient, scalable channel of organic growth that will deliver a significantly lower cost per policy, a significantly shorter time to resolve claims, a significantly greater number of conversions and a significantly better customer experience.
Schedule a complimentary consultation with TokenMinds to explore how your organization can integrate AI and blockchain to modernize bancassurance operations, reduce friction, and unlock sustainable revenue growth.
FAQ
1. What issues does blockchain and AI address in bancassurance?
They enable automatic coordination of bank/insurer interactions, including automated underwriting and claims validation, through automation of all reconciliation processes; ai provides immediate decision-making capabilities with blockchain providing immutable record-keeping mechanisms that prevent parties from disputing ai generated outcomes.
2. Why would blockchain be needed to correct bancassurance inefficiencies, if only AI was used?
Although ai can evaluate data and generate predictions, it has no capability to either enforce terms of insurance policies, nor to facilitate payments for claims independent of blockchain execution.
3. In what ways will blockchain minimize costs associated with reconciliation and disputes?
A single shared ledger (blockchain) created by the parties involved allows banks and insurers to view the same information on policies, premiums, and claims in near real-time, eliminating duplicate entry, reducing version conflicts, and decreasing the need for manual reconciliation.
4. How will smart contracts expedite claims processing?
Smart contracts will automatically implement claims when specified conditions have been fulfilled (e.g., event verification, ai approved fraudulent activity); this will greatly reduce the time from days to minutes for settlement of claims, eliminating the need for manual approvals.
5. In what manner does AI contribute to the underwriting and fraud detection process?
AI models will continually provide recommendations regarding the types of insurance products based on individual risk assessments; they will also identify potential fraudulent activity by analyzing an individual’s transactional history, customer behavior, and other external sources of information; these models will continually improve their ability to perform these functions as more data becomes available.
6. Is this model viable for financial institutions that are subject to regulatory oversight?
Yes. permissioned blockchains, auditable smart contract functionality, explainable ai models, and role-based access control mechanisms allow financial institutions to satisfy regulatory obligations related to compliance and reporting.








